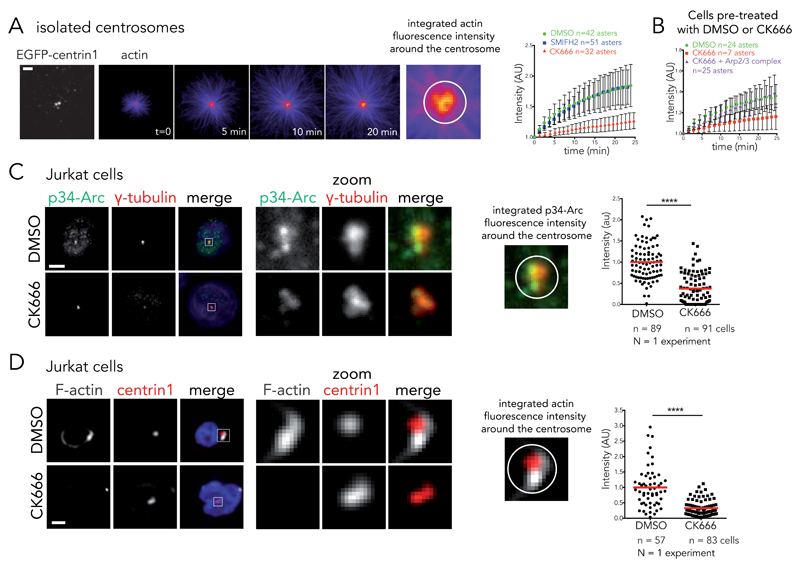
Figure 5. Arp2/3 complex inactivation impairs actin filament nucleation at the centrosome.
(A) Time-lapse imaging of actin filament assembly from isolated centrosomes. “Fire” look-up table of actin images reveals that fluorescence intensity increases at the centrosome over time. This intensity was integrated over a 2 μm diameter circle around the centrosome and plotted against time in the presence of DMSO, 0.2 mM SMIFH2 or 0.2 mM of CK666 (right panel). Intensities were normalized with respect to initial intensity. Data show the results of a single experiment, representative of 3 independent experiments. Errors bars represent standard deviation. Scale bar: 5 μm. (B) Actin nucleation activity for centrosomes isolated from DMSO or CK666-treated cells. Addition of 100 nM purified Arp2/3 complex restores nucleation activity of CK666-treated centrosomes. Data show the results of a single experiment, representative of 3 independent experiments. Errors bars represent standard deviation. (C) Immunostaining of p34-Arc (green), γ-tubulin (red) and DNA (blue) at the centrosome of Jurkat cells incubated with DMSO or 0.2 mM CK666 and subsequently fixed with cold methanol. Right panel: p34-Arc fluorescence integrated over a 3 μm diameter circle around the centrosome for DMSO and CK666 condition. **** p ≤ 0.0001. Scale bar: 5 μm. (D) Immunostaining of F-actin (phalloidin, white) at the centrosome (EGFP-centrin1, red) of Jurkat cells incubated with DMSO or 0.2 mM CK666 and subsequently treated with detergent prior to PFA fixation. Actin fluorescence intensity was integrated over a 4 μm diameter circle around the centrosome to compare the two conditions (right panel). **** p ≤ 0.0001. Scale bar: 5 μm. Red bar indicates the mean. Unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction was used to generate p values.