Figure 2.
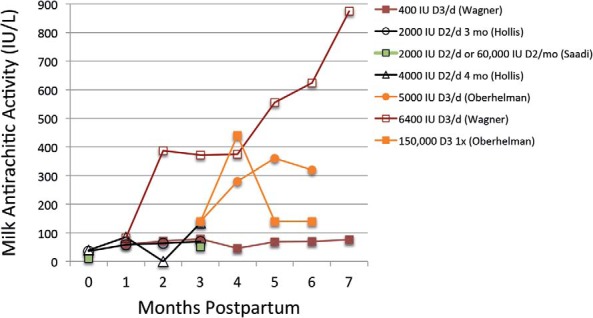
Double-blind RCTs have shown that maternal intakes of 1000–6400 IU/d of vitamin D are associated with increased breast milk vitamin D concentrations (156, 168, 169, 171). Lines of similar color represent the same study, and the legend provides the vitamin D supplementation dose (IU/d unless otherwise stated). Oberhelman et al (171) reported milk concentrations of cholecalciferol only.
