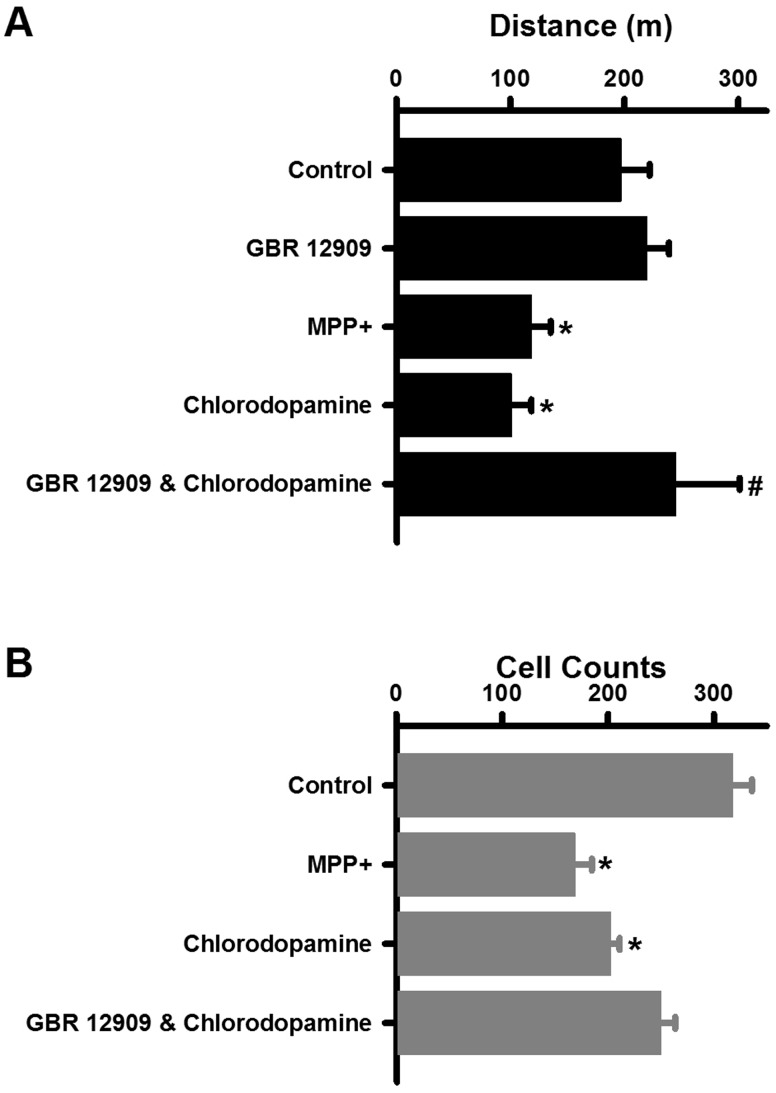
FIG. 9.
Chlorodopamine causes neuronal loss and behavioral deficits in vivo. Behavioral changes due to these treatments are indicated by the distance traveled by the mice 3 days after the intrastriatal injections (A). Significant difference from control is denoted by * for P values <.05. Similarly, the significant difference between the chlorodopamine and GBR 12909 + chlorodopamine groups at P <.05 is indicated by #. Changes in the density of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra (mean ± SEM) are indicated by the tyrosine hydroxylase staining of tissues taken from animals 3 days following 2 μl intrastriatal injections consisting of artificial cerebrospinal fluid (control, n = 13), 90 nmol MPP + (n = 12), 90 nmol chlorodopamine (n = 11), or chlorodopamine to mice pretreated with 10 μg/kg GBR12909 (n = 10) is depicted in panel (B). Significant difference from control is denoted by * for P values <.05. These differences were determined as described in the Methods section.