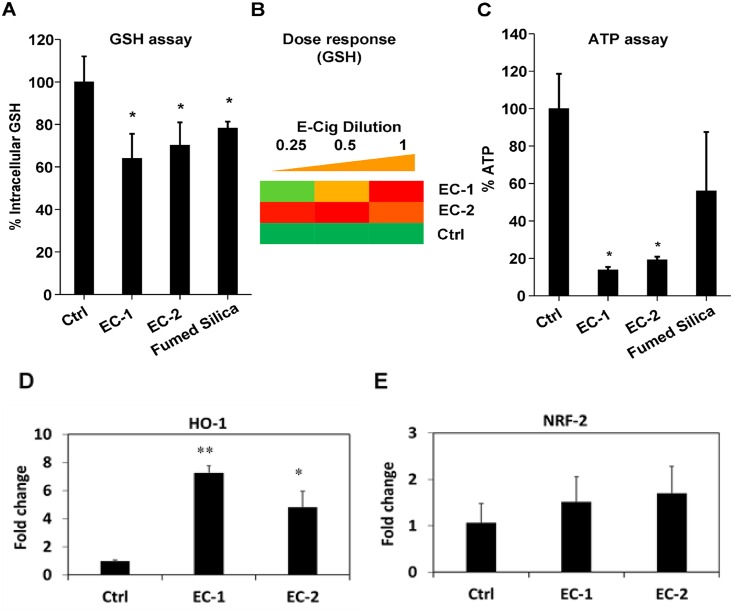
Fig 5. Oxidative stress and cytotoxicity induced by EC aerosols in NHOKs.
(A) Intracellular GSH levels in NHOKs after exposure to EC aerosols. NHOKs were exposed to EC aerosols for 24 h and intracellular GSH levels were determined using a GSH-Glo assay. Fumed silica (100 μg/ml) was used as a positive control. *p<0.05 compared to untreated control cells. (B) Heat maps to show the dose-dependent increase in oxidative stress induced by EC in NHOKs. Conditions are the same as (A). (C) Cell viability of NHOKs after exposure to EC aerosols for 24 h was determined using ATP assay. The cell viability of the EC-treated cells was normalized to the value of non-treated control cells, for which the viability was regarded as 100%. Fumed silica (100 μg/ml) was used as a positive control. *p<0.05 compared to untreated control cells. (D&E) qPCR analysis of heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) and nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF-2) expression in NHOKs after exposure to EC aerosols. *p<0.05; ** p<0.01 compared to untreated control cells.