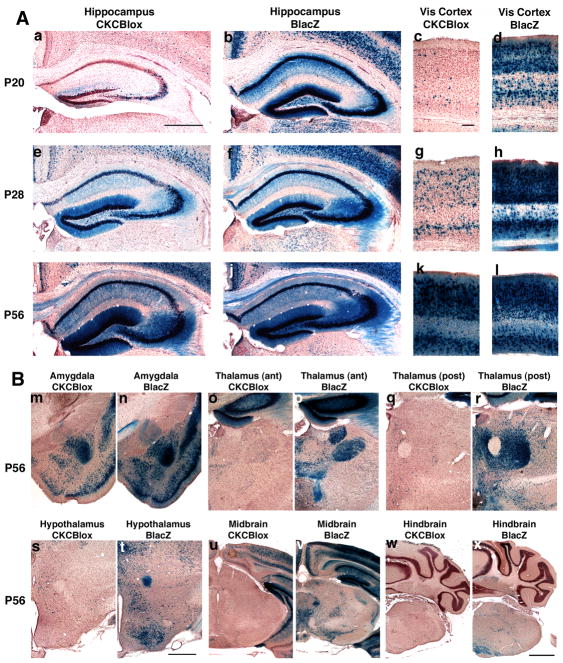
Fig 1.
1A Postnatal development of recombination is driven by CaMKcre in hippocampus and visual cortex (Vis cortex) of BDNFlox/+ mice. Sections from CaMKcre; BDNFlox/+ (CKCBlox) mice (a,c,e,g,i,k) and BDNFlacZ/+ (BLacZ) mice (b,d,f,h,j,l) were stained with X-gal and counter-stained with neutral red. Slices shown are rostral hippocampus (a,b,e,f,i,j), and visual cortex (c,d,g,h,k,l). Panels are from mice aged postnatal day 20 (a,b,c,d), P28 (e,f,g,h), and P56 (i,j,k,l) . Scale bar in panel a is 500μm for all hippocampal images, scale bar in panel c is 100μm for all visual cortex panels.
1B Substantial recombination is apparent in amygdala, but not thalamus, hypothalamus, midbrain or hindbrain of CaMKcre; BDNFlox/+ mice at 8 weeks. Sections are from 8 week old CaMKcre; BDNFlox/+ (CKCBlox) mice (m,o,q,s,u,w) and BDNFlacZ/+ (BLacZ) mice (n,p,r,t,v,x). Slices shown are amygdala (m,n), anterior thalamus (o,p), posterior thalamus (q,r), hypothalamus (s,t), midbrain (u,v) and hindbrain (w,x). Scale bar in panel t is 500μm for amygdala, hypothalamus and thalamus panels, scale bar in panel x is 1mm for midbrain and hindbrain images.