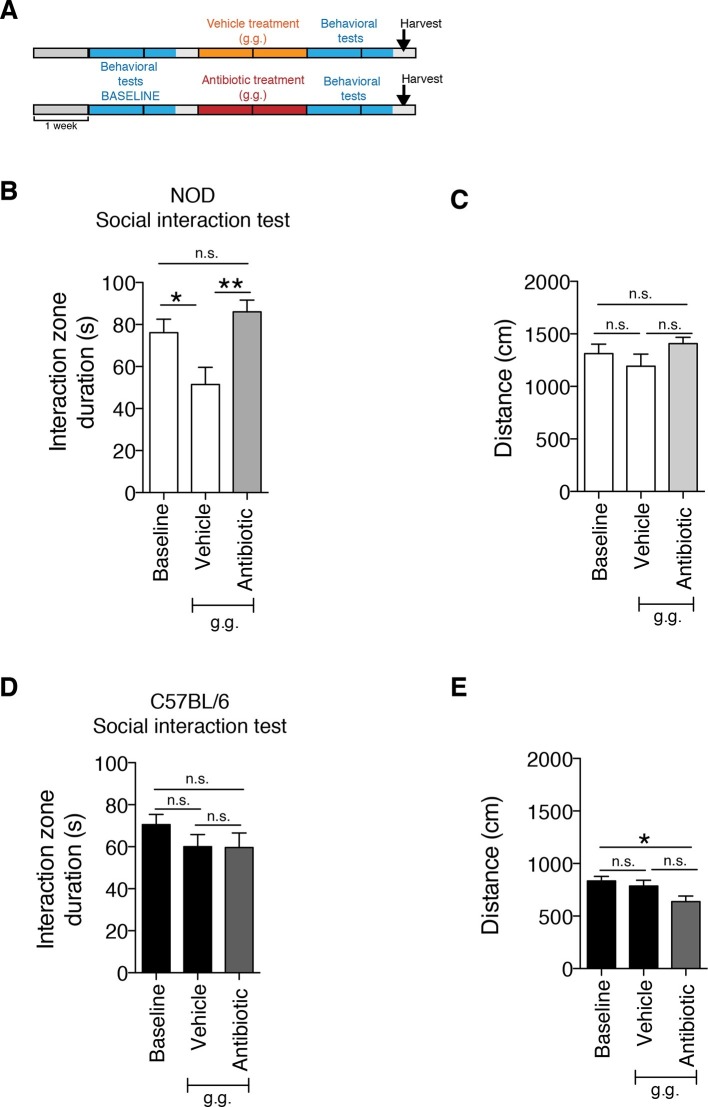
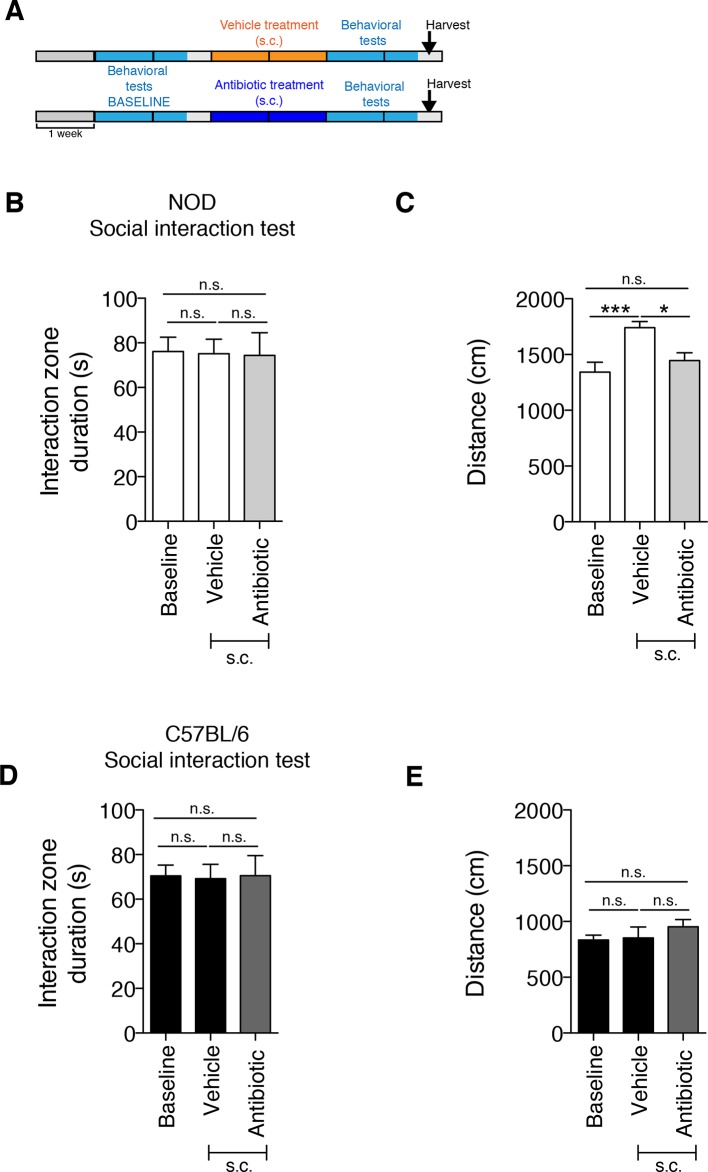
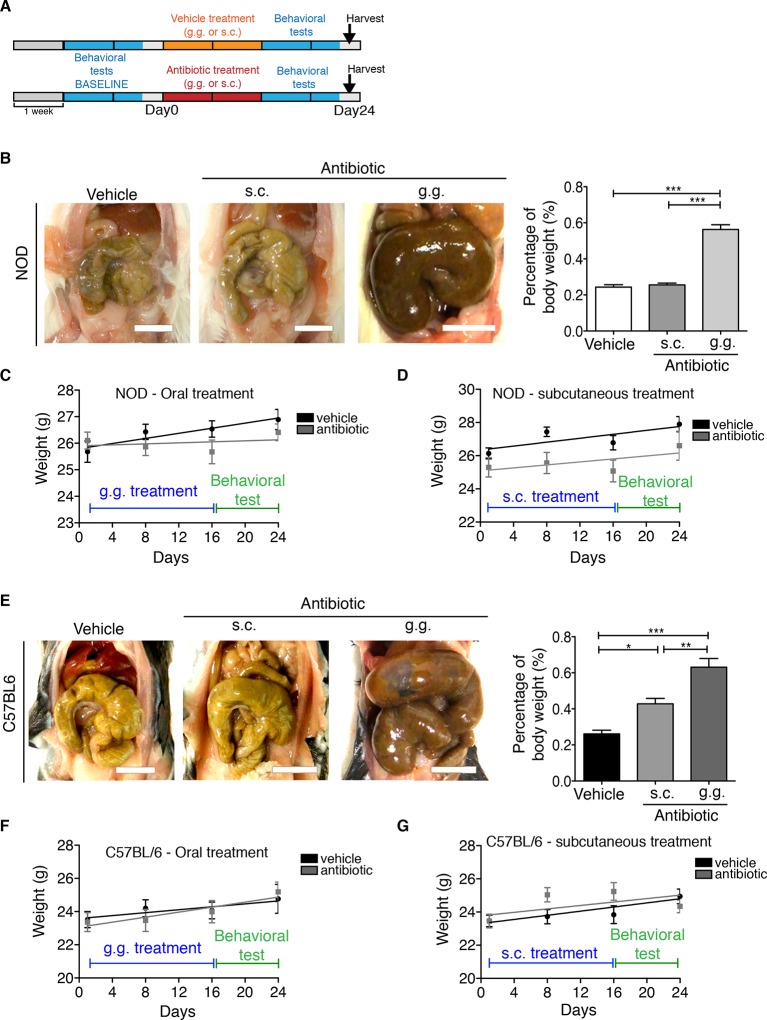
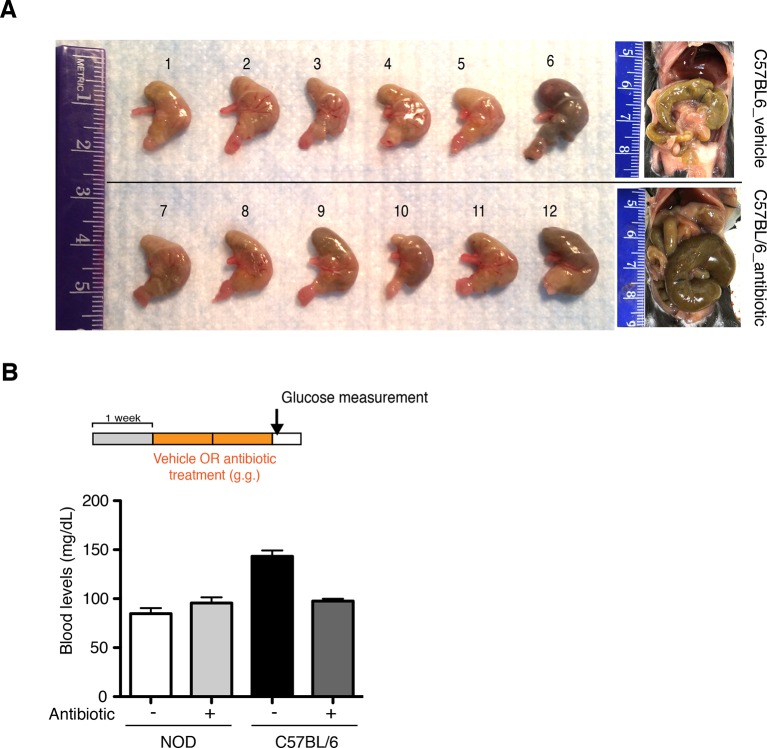
Figure 1. The strain-specific social avoidance behavioral response to daily gavage is affected by oral antibiotic treatment.
(A) Experimental timeline: vehicle or antibiotic mix were administered daily by gastric gavage (g.g.) for 14 days. Behavioral testing was performed before (baseline) and after treatment. (B–D) Results of the Social Interaction (SI) test for NOD (B) and C57BL/6 (D) mice. Oral antibiotic treatment did not affect locomotor activity measured during the social interaction test (C,E) (3 independent experiments with 8 mice per group/experiment for a total of n=23–24 mice per condition). Data are mean ± S.E.M; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 based on one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test; n.s. indicates not significant.