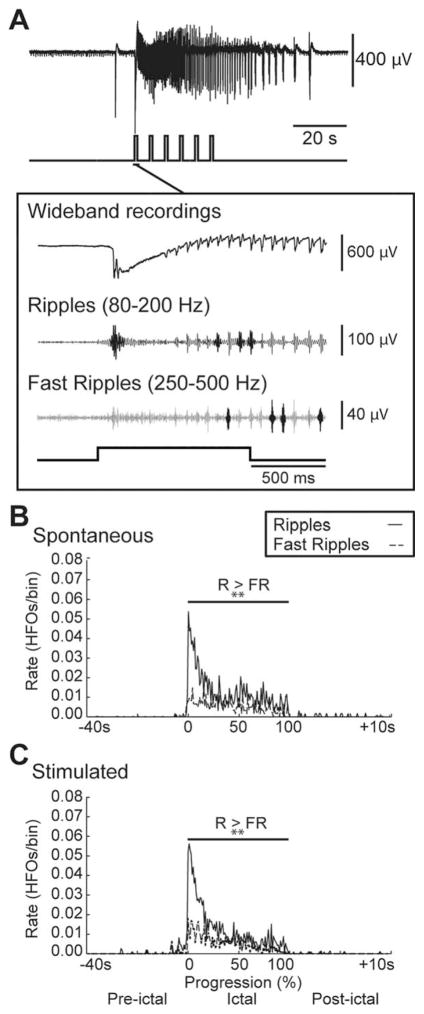
FIGURE 3.
Similar patterns of high-frequency oscillations (HFOs) characterize spontaneous and light-triggered ictal discharges. (A) Ictal discharge stimulated by a train of 1-second light pulses and expanded onset illustrating wide-band recording and filtered traces of associated ripples and fast ripples that are highlighted in darker gray. (B, C) Average rate of ripples (R) and fast ripples (FR) in the 40 seconds preceding, during, and 10 seconds following spontaneous (n=9 events) and stimulated (n=10 events) ictal discharges, respectively. The duration of the ictal discharges was normalized with 0 representing their start and 100 representing their end. Note that ripple rates are higher than fast ripple rates throughout spontaneous and stimulated ictal discharges as well as that both types of HFO are characterized by highest rates at the onset of the event and gradually decrease throughout the event; **p< 0.01.