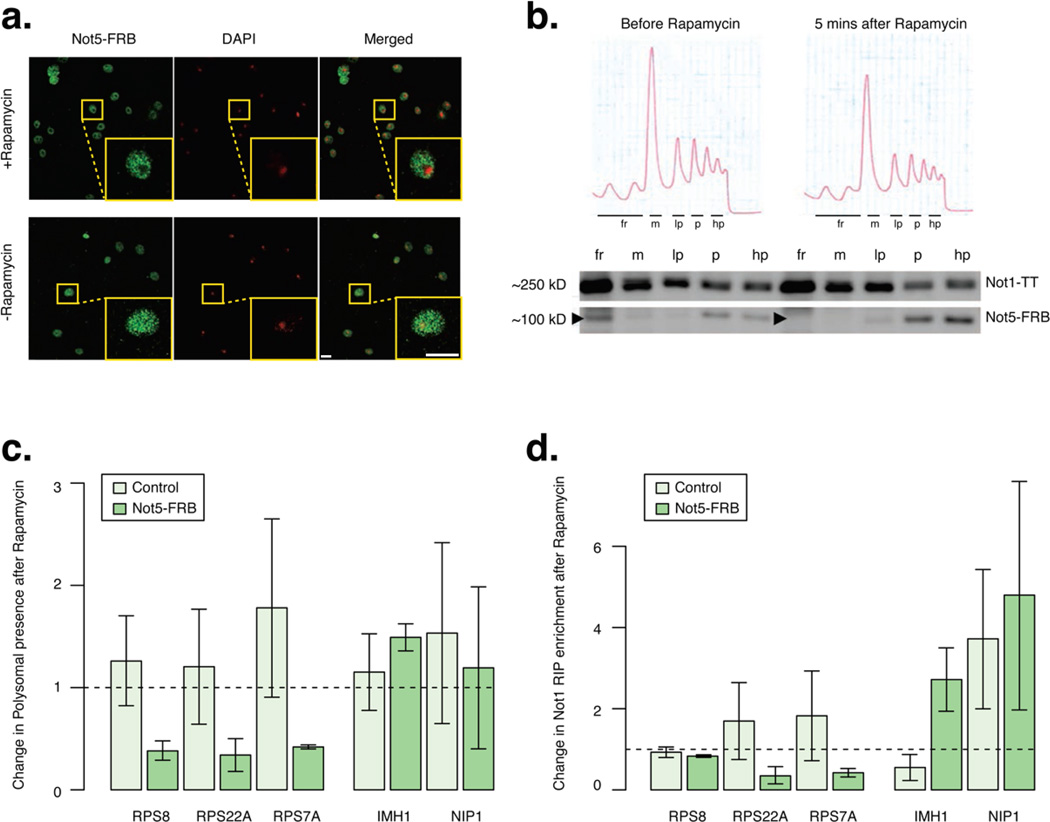
Figure 7. Translatability of specific mRNAs is regulated by nuclear Not5.
Tethering of Not5 to the cytoplasm leads to reduced presence of RP encoding-mRNAs and increased presence of IMH1 mRNA in polysomes. a: Localization of FRB-fused Not5 in cells before and after treatment for 5 minutes with rapamycin. Nucleus is shown in red (DAPI), Not5-FRB is shown in green (Alexa-fluor). In response to rapamycin nuclear localization of Not5-FRB was lost and the nuclei are detected as dark holes, which co-localize with DAPI staining. Scale bars represent 5 µm b: Presence of Not5-FRB and Not1 before and after 5 minutes rapamycin treatment in free fractions (fr), monsomes (m), and in 3 polysome fractions, light (lp), medium (p) and heavy (hp). Arrows indicate Not5-FRB. Polysome traces before and after rapamycin treatment for 5 minutes are displayed above the corresponding blots.
c: Barplots of the change in abundance of several mRNAs in polysomes after treatment for 5 minutes with rapamycin in control cells, or cells expressing Not5-FRB.
d: Barplot for fold change in Not1 RIP enrichment over total extract after rapamycin compared to before for several mRNAs, in control cells and in cells expressing Not5-FRB. c–d, error bars representing SD. See also Figure S6 and Table S4.