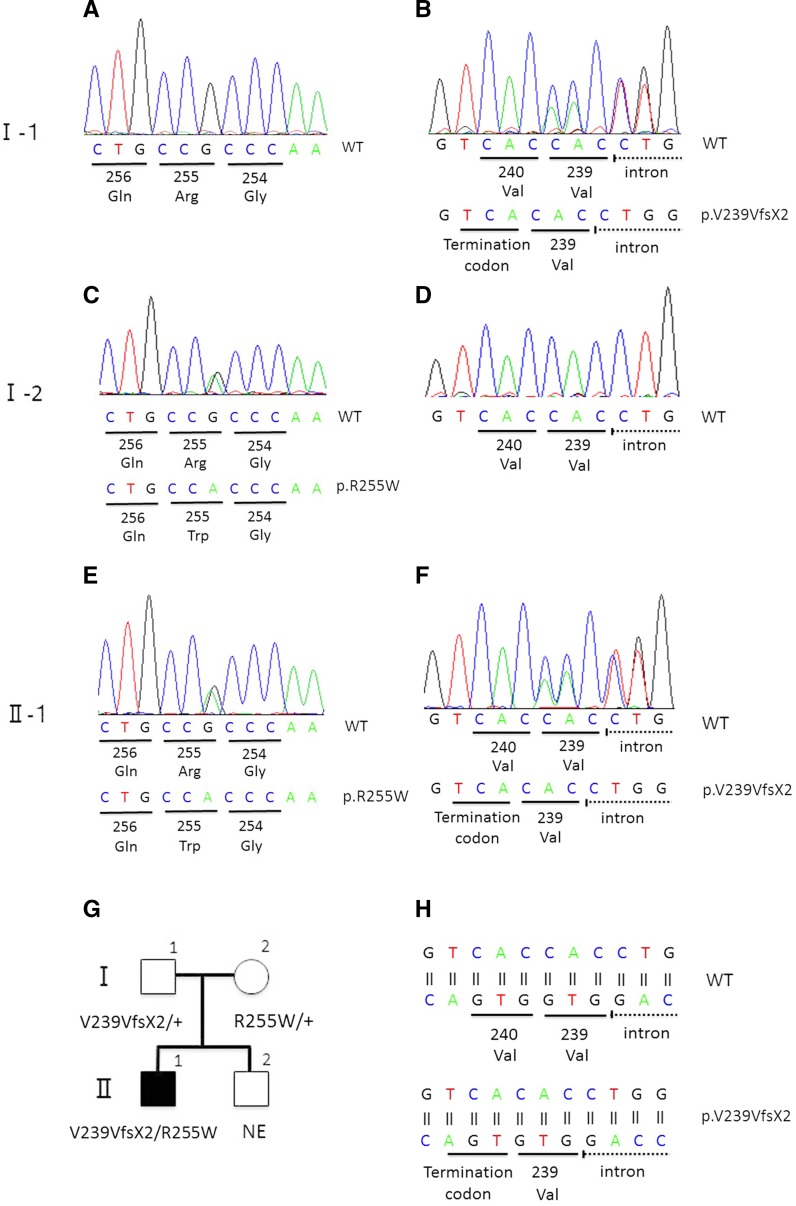
Fig. 5.
Molecular genetic findings and a pedigree chart. Sequence chromatograms of the proband’s father (I-1; a, b), mother (I-2; c, d), and the proband (II-1; e, f) are shown. Sequence chromatograms around the amino acid position 255 (a, c, e) and 240 (b, d, e) are shown. Results of reverse strand of the sequence chromatograms are shown (a–f). A single-nucleotide mutation (c.763C>T) results in the substitution of tryptophan for arginine at amino acid position 255 (p.R255W) in the mother and proband (c, e). A deletion mutation (c.717delG) results in the synonymous substitution of valine for valine at amino acid position 239 and a frame shift that leads to a premature termination codon at two amino acid residues downstream from the mutation (p.V239VfsX2) in the father and proband (b, f). Pedigree charts for the segregation analysis are shown (g). Schematic diagram of the deletion mutation (c.717delG) in the proband (bottom) and wild type (top) are shown (h). A frame shift mutation leads to a premature termination codon at two amino acid residues downstream from the mutation