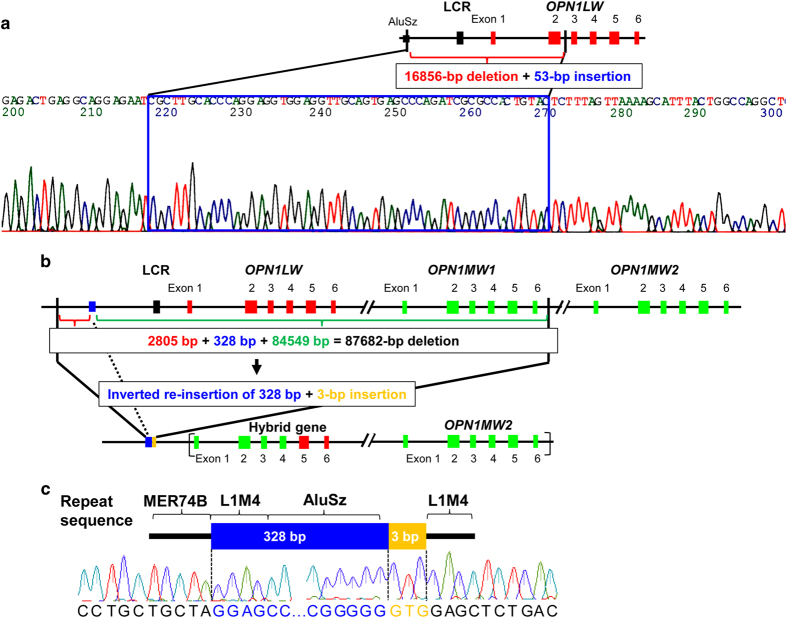
Figure 3.
Determination of the region surrounding the deletion breakpoints in two Japanese families with blue cone monochromacy (BCM). (a) Precise analysis of the deletion–insertion mutation by junction PCR and sequencing in case BCM1. Genomic structure of human OPN1LW. The red and black boxes represent OPN1LW exons and locus control region (LCR), respectively. BCM1 had a 16,856-bp deletion and 53-bp insertion. The proximal and distal boundaries of the deletion were 8,899 bp upstream of the OPN1LW translation initiation codon and within OPN1LW intron 2, respectively. The proximal boundary of the breakpoint was an AluSz repeat sequence, and the 53-bp insertion contained a partial Alu repeat sequence. (b) Precise analysis of the deletion–inversion–insertion mutation by genomic walking in case BCM2. Genomic structure of human OPN1LW and OPN1MW. Red and green boxes represent OPN1LW and OPN1MW exons, respectively; the black box represents the LCR. BCM2 had an 87,682-bp deletion, an inverted re-insertion of 328 bp that is a part of the deleted sequence and a 3-bp insertion. The proximal and distal boundaries of the deletion were 28,144 bp upstream of the OPN1LW initiation codon and 7764 bp downstream of the OPN1MW1 translation termination codon, respectively. In BCM2, exons 2 and 4 of OPN1LW were absent, whereas the presence of exon 5 in OPN1LW and OPN1MW2 were confirmed. It is possible that BCM2 harbored a normal OPN1MW2 as well as a hybrid gene comprising OPN1MW2 exons 1–4 joined to OPN1LW exons 5 and 6. The brackets indicate that this structure is one of possibilities including the order of the hybrid gene and OPN1MW2. (c) Diagram and electropherogram of the region surrounding deletion–inversion–insertion breakpoints in BCM2, which were located within highly repetitive sequences.