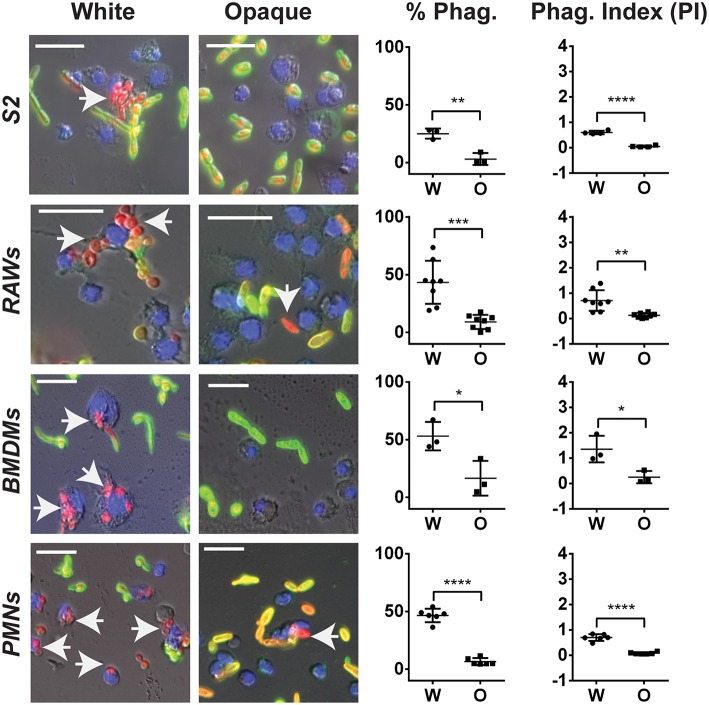
Figure 7.
C. albicans white cells are phagocytosed more efficiently than opaque cells by macrophages in vitro. The indicated immune cell type was incubated with C. albicans white (CAY4975) or opaque (CAY4986) cells for 30 min to 2 h (see Methods) at 28°C (S2 cells) or 37°C (RAWs, BMDMs, and PMNs) and imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Blue (Hoechst) staining represents macrophage nuclei, internalized C. albicans appear red (dTomato label), and extracellular C. albicans are stained both green (using an anti-C. albicans antibody) and red. Arrows point to phagocytosed cells. The percent phagocytosis (total number of macrophages that have phagocytosed ≥ 1 C. albicans cell divided by the total number of macrophages scored) and phagocytic index (PI) (total number of C. albicans cells phagocytosed divided by the total macrophages scored) were quantified for both white (W) and opaque (O) cells. Data is represented as the mean ± SD and each dot represents a single biological replicate that was assayed in triplicate. At least 100 macrophages were quantified per assay. A Student's t-test was performed to determine statistically significant differences between the two groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; and ****p < 0.0001. Arrows represent internalized C. albicans. Scale bars, 20 μm.