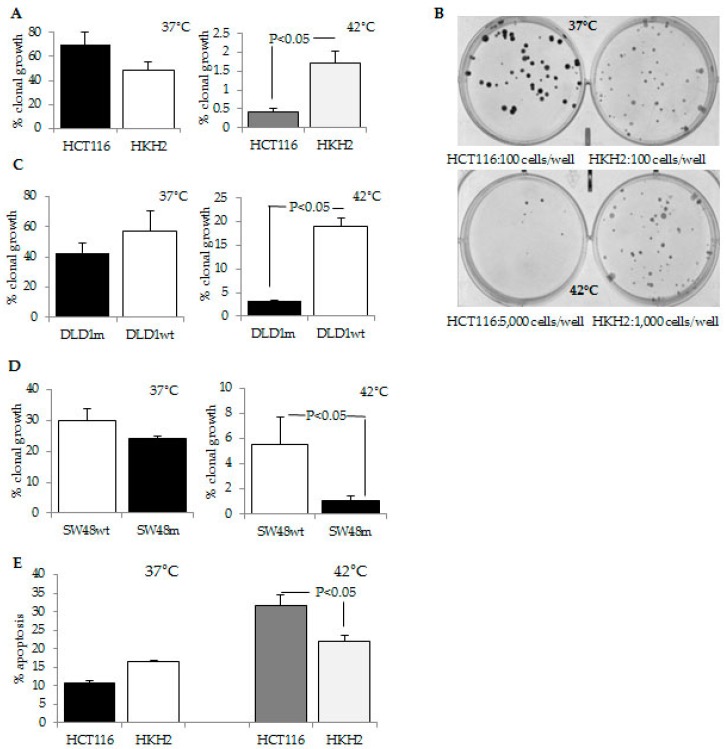
Figure 1.
Differential hyperthermia response of mutant and wild type KRAS CRC cells. (A) Clonal growth assays. Cells were plated at 100 per well in six-well plates and incubated at 37 °C for two weeks, or at 5000 cells/well (HCT-116) and 1,000 cells/well (HKH2), incubated at 42 °C for 24 h, and transferred to 37 °C for two weeks. The percent clonal growth is the ratio of number of colonies to number of all plated cells, multiplied by 100; (B) Representative results from clonal growth analyses described in (A); (C) Isogenic DLD-1m cells (with a mutant KRAS,G12D) and DLD-1wt (DLD-1 cells with a wild type KRAS) were exposed to 37 °C or 42 °C for 24 h, and clonal growth was measured as described in (A); (D) Isogenic SW48wt cells (with a wild type KRAS) and SW48m (with a KRAS mutation G12D) were assayed for clonal growth as described in (A). All clonal growth assays were performed with triplicate samples per treatment conditions; three to five assays were performed at each temperature; (E) Cells were exposed to 37 °C or 42 °C for 24 h. All cells (floating and attached) were harvested and stained for apoptotic and necrotic markers with R-phycoerythrin (PE)––Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). Four experiments with triplicate samples per treatment were performed.