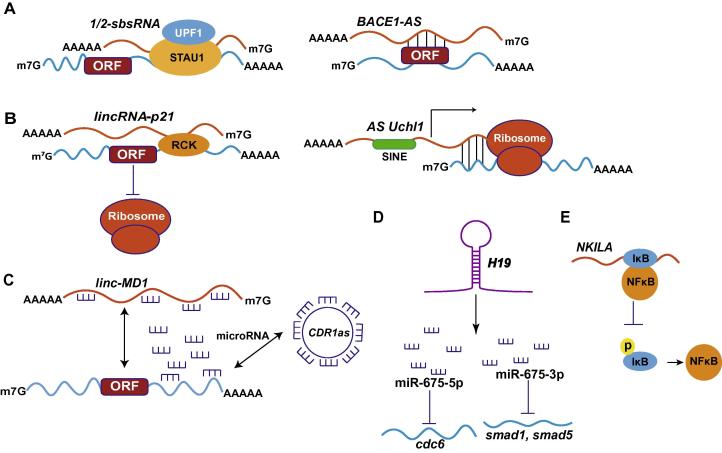
Figure 1.
Known working models of cytoplasmic lncRNA function
A. lncRNAs modify mRNA stability, with 1/2-sbsRNA as an example of decreasing the stability of mRNA and BACE1-AS as an example of increasing the stability of mRNA. B. lncRNAs regulate mRNA translation, with lincRNA-p21 as an example of inhibiting the translation and AS Uchl1 as an example of promoting translation. C. lncRNAs modulate gene expression by functioning as ceRNAs, with linc-MD1 as well as CDR1as shown as examples. D. lncRNAs can give rise to microRNAs, with H19 shown as an example. E. Some lncRNAs affect protein modification, with NKILA as one of such kind of cytoplasmic lncRNAs. ORF, open reading frame; 1/2-sbsRNA, half-STAU1-binding site RNA; BACE1-AS, antisense transcript for β-secretase 1; linc-MD1, long non-coding RNA muscle differentiation 1; CDR1as, cerebellar degeneration-related protein 1 antisense transcript; NKILA, NF-κB interacting lncRNA; AS Uchl1, antisense transcript for ubiquitin carboxy terminal hydrolase L1; SINE, short interspersed element; cdc6, cell division cycle 6.