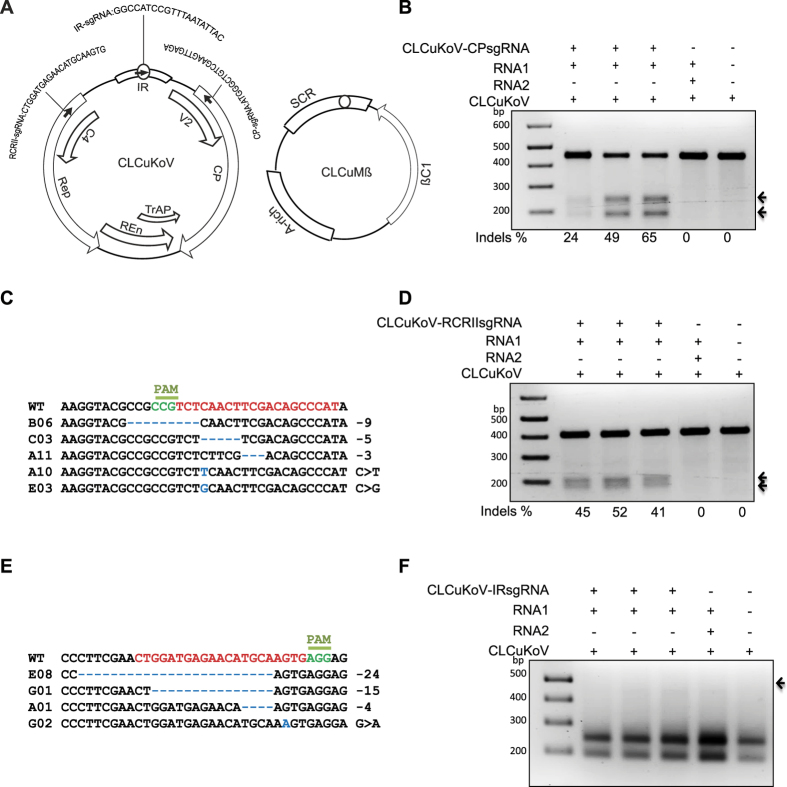
Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeting of coding and non-coding sequences of the CLCuKoV genome.
(A) Genome organization of CLCuKoV and CLCuMß. Bidirectional and overlapping ORFs (CP, Rep, Ren, TrAP, V2, and C4) are represented by arrows, the IR by a box, stem loop nonanucleotides by a small circle in the IR and SCR, and targets by arrowheads and individual sequences. The selected targets, one in non-coding IR, one each in coding CP or in the Rep RCRII domain, were analyzed for CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeting (B) NHEJ repair (indel) analysis via the T7EI assay. Arrow indicates the presence of 255 bp and 191 bp regions only in samples expressing CP-sgRNA, but not in samples with TRV empty vector or virus alone. (C) Alignment of PCR amplicons encompassing the CP region and subjected to Sanger sequencing for indel (NHEJ repair) confirmation. (D) T7EI assay detecting indels in the RCRII domain of CLCuKoV genome. Mutations were detected only in RCRII PCR amplicons from plants infiltrated with TRV containing RCRII-sgRNA, but not in plants infiltrated with TRV empty vector or virus alone. (E) Alignment of PCR amplicons encompassing the RCRII motif and subjected to Sanger sequencing for NHEJ repair confirmation. (F) NHEJ repair analysis at the IR sequence by restriction site loss assay. The arrow indicates the expected SspI-resistant 446 bp DNA fragment; none of the samples produced the SspI-resistant DNA fragment, which is similar to TRV empty vector or virus alone. Arrows in (A), (C) and (E) represent the expected DNA fragments. The indel percentage shown was calculated based on the Sanger sequence reads. In (B) (reverse strand sequence) and (D) the wild-type (WT) sequences are shown at the top (target sequence is shown in red; the protospacer-associated motif [PAM] in green, followed by the various indels formed, as indicated by numbers to the right of the sequence (−, deletion of x nucleotides; + , insertion of x nucleotides; and > , change of x nucleotides to y nucleotides). CP coat protein, Rep replicase, Ren replication enhancer, TrAP transcriptional activator protein, βC1 betasatellite conserved ORF, IR intergenic region, SCR satellite conserved region.