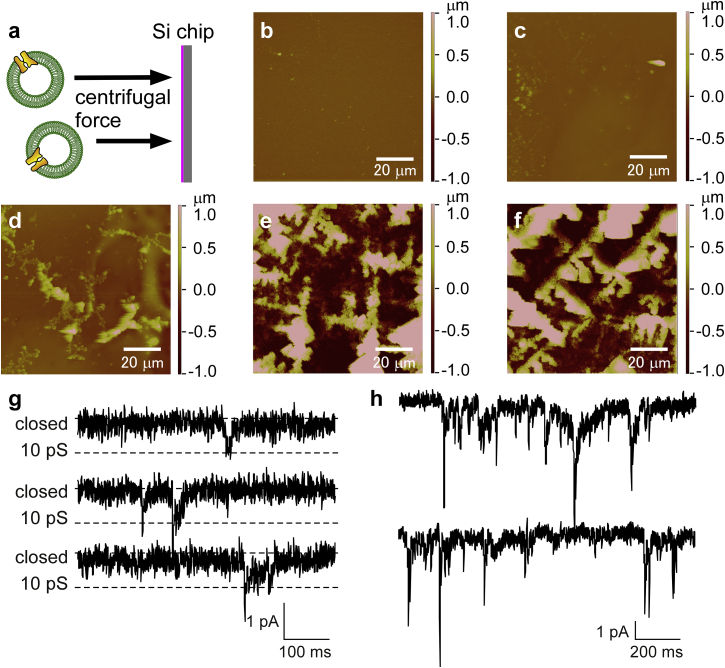
Figure 2.
Centrifugal force as a driving force to improve the accessibility of membrane vesicles to BLMs. (a) Si chips with no apertures were centrifuged in the presence and absence of membrane vesicles containing hERG channels. (b–f) The surface topography of the chips after centrifugation was analyzed by AFM. Conditions for centrifugations: (b) 1000 rpm for 10 min without membrane vesicles, (c) 300 rpm for 30 min with membrane vesicles containing hERG channels, and (d–f) 10 min centrifugation with membrane vesicles containing hERG channels at (d) 500 rpm, (e) 800 rpm, and (f) 1000 rpm. The middle area (90 μm × 90 μm) of the Si chip was scanned. This area covers the region of the BLMs (Φ: 18–55 μm) in the case of Si chips suspending BLMs. (g) Example of single hERG channel currents recorded after centrifugation at 500 rpm for 10 min. The applied potential was −100 mV. (h) Example of multiple hERG channel currents recorded after centrifugation at 500 rpm for 10 min. The applied potential was −100 mV. To see this figure in color, go online.