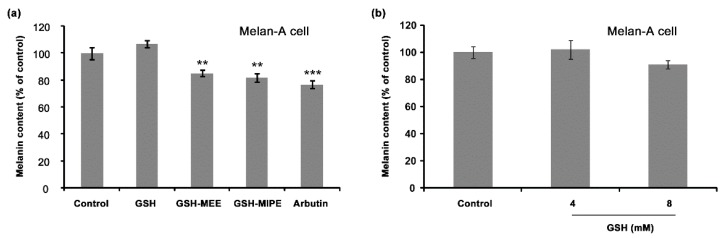
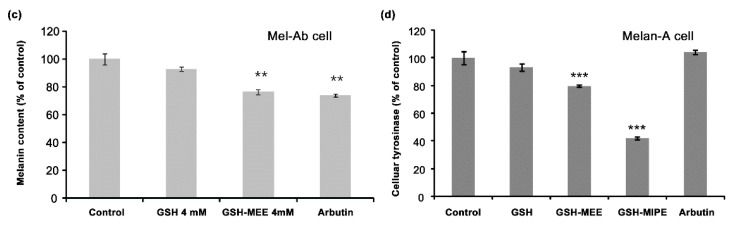
Figure 2.
(a) Effect of GSH derivatives on melanin content in Melan-A cells. GSH exhibited no inhibitory effect on melanin production, but GSH-MEE and GSH-MIPE decreased the melanin synthesis in Melan-A cells. Arbutin (100 µg/mL) was treated to serve as a positive control. The melanin content was calculated by normalizing the melanin content to total cellular protein and reported as a percentage of control. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of three replicates, and ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001. GSH, reduced glutathione; GSH-MEE, GSH monoethyl ester; GSH-MIPE, GSH monoisopropyl ester; SD, standard deviation; (b) The effect of GSH on melanin production in Melan-A cells. GSH had no inhibitory effect on melanin production in Melan-A cells. Each sample was quantified with the same amount of protein and reported as a percentage of control. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of three replicates; (c) Effect of GSH and GSH-MEE on melanin content in Mel-Ab cells GSH had no inhibitory effect on melanin production, but GSH-MEE decreased the synthesis of melanin significantly in Mel-Ab cells. Arbutin (100 µg/mL) was treated as a positive control. The melanin content was calculated by normalizing the melanin content to total cellular protein and reported it as a percentage of control. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of three replicates, and ** p < 0.01; (d) the effect of GSH derivatives on intracellular tyrosinase activity in Melan-A cells. GSH had no significant effect on intracellular tyrosinase activity, but GSH-MEE and GSH-MIPE decreased the activity of intracellular tyrosinase in Melan-A cells. Arbutin (100 µg/mL) was treated as a positive control. Each sample was quantified with the same amount of protein and reported as a percentage of control. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of three replicates, and *** p < 0.001.