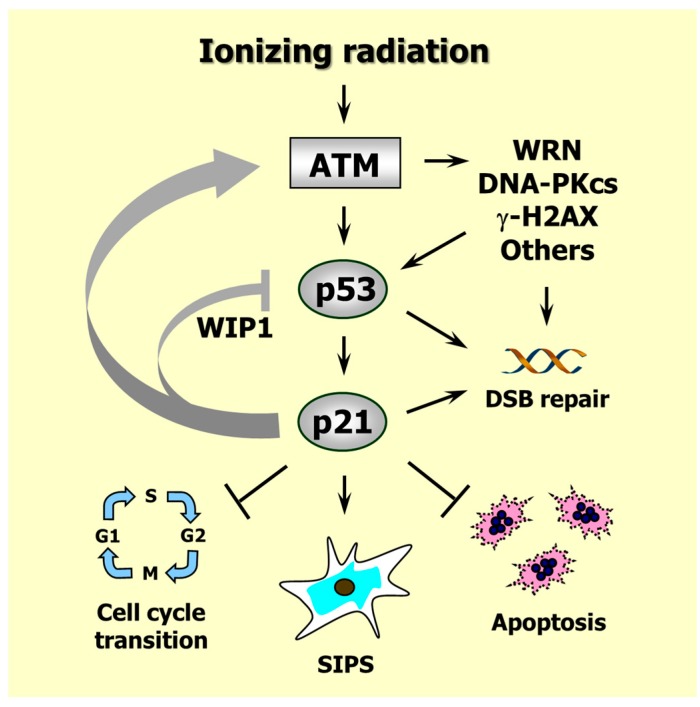
Figure 5.
Responses induced by ionizing radiation in p53 wild-type human solid tumor-derived cell lines. Arrows indicate stimulation and T-shaped lines indicate inhibition. Radiation exposure results in ATM-dependent activation of several proteins (e.g., p53, WRN, DNA-PKcs) that play important roles in DSB repair, as well as p53-mediated activation of p21 that suppresses apoptosis and activates cell cycle checkpoints. Proper activation of these events provides time for the repair of potentially cytotoxic and mutagenic lesions. Persistence of DNA damage leads to sustained induction of p21 which downregulates p53 (e.g., through WIP1), suppresses apoptosis and triggers SIPS. Positive feedback loops between ATM and p21 ensure the maintenance of the SIPS response for extended times (e.g., several months in culture). For further details, consult [31,37]. WRN, Werner’s syndrome protein; DNA-PKcs, DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit; γ-H2AX, H2A variant histone H2AX phosphorylated on Ser 139; WIP1, wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1.