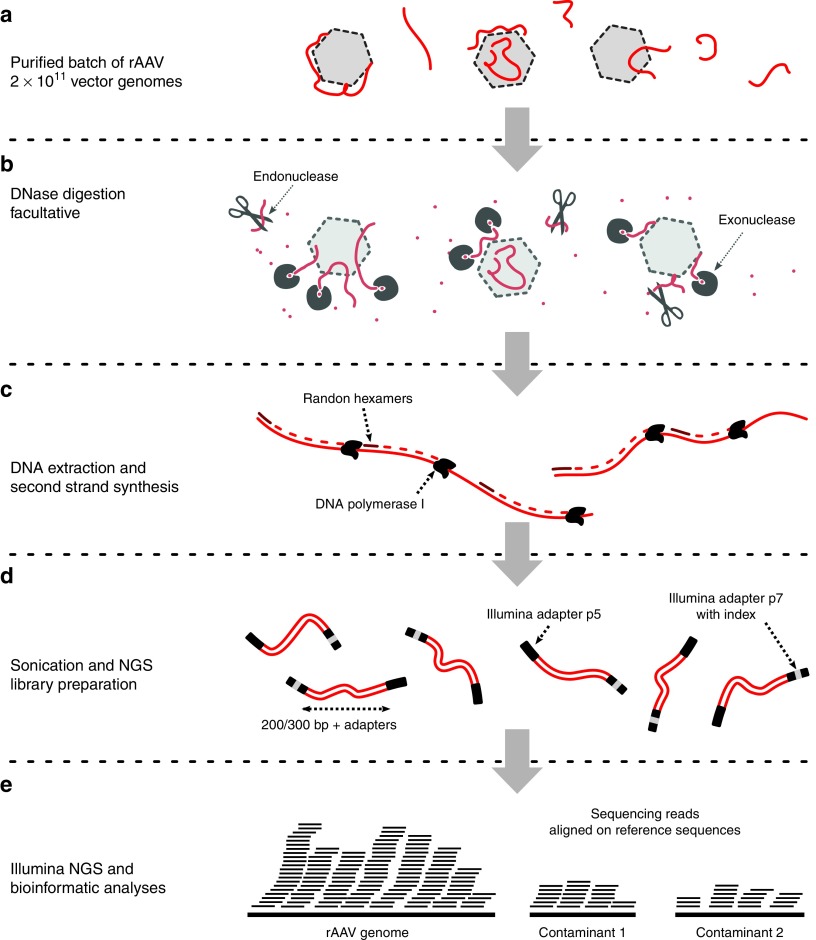
Figure 1.
Overview of SSV-Seq protocol. (a) A quantity of 2 × 1011 vector genomes of a purified rAAV preparation are required as input. (b) To reduce the amount of nonencapsidated DNA, eventually, a DNase digestion step can be performed, with a mix of highly efficient DNases (Baseline-ZERO and Plasmid-Safe DNases). (c) After DNA extraction, total DNA is denatured, and the second strand is synthesized by random priming with the high-fidelity Escherichia coli DNA Pol I, followed by a purification step. (d) The dsDNA template is sheared by sonication into 200–300 bp fragments, which are subsequently end-repaired and A-tailed to allow for the ligation of adaptors compatible with Illumina sequencing. One of the two adaptors contains a short DNA barcode, also called an “index”, which is different for each experimental sample. Finally, an optimized PCR amplification is performed. All of the library preparation steps are checked by chip electrophoresis. (e) A qPCR-based quantification of next-generation sequencing libraries is performed prior to pooling for cluster generation on flow cell in the presence of nonindexed ϕ-X DNA. High-throughput sequencing is achieved on an Illumina HiSeq platform (Rapid Run 2 × 101 bp). Finally, ContaVect performs automated bioinformatic analyses, including preprocessing of reference and sequencing reads, attribution of reads to a reference sequence and postprocessing, resulting in several simple reports.