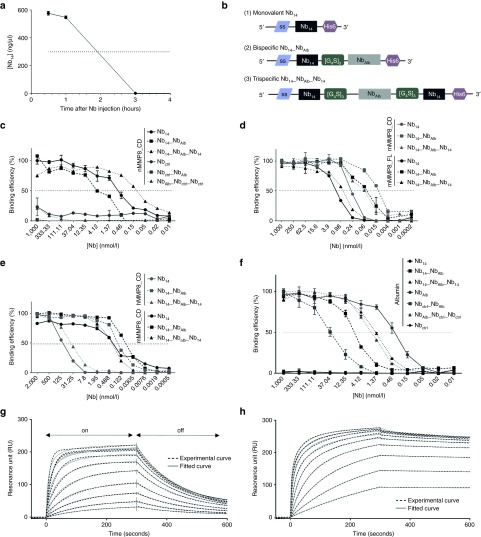
Figure 2.
Pharmacokinetic properties of the MMP8-binding Nb14 and binding capacity of the modified multivalent Nb14. (a) Serum Nb levels at different time points after intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) injection of 100 µg of the monovalent Nb14 in mice (n = 10) (T1/2 Nb14, 2 hours). (b) A schematic overview of the different Nb14 constructs shows that all constructs contain a C-terminal His6 tag for purification and detection purposes and an N-terminal signal sequence (ss) that is removed after secretion. (1) The monovalent Nb14 is cloned into the pHEN6C vector and contains a pelB signal sequence for Nb protein secretion in the periplasmic space of bacteria. (2) The bispecific Nb14_NbAlb contains an anti-albumin binding Nb connected to Nb14 via a flexible linker ([G4S]3). It was cloned in the pHEN6C (pelB) for protein production in bacteria and in the pCAGGs vector for electroporation as cDNA. The pCAGGs vector contains a sigal sequence that leads to secretion of the Nb out of the electroporated cells. (3) The trispecific Nb14_NbAlb_Nb14 contains two flexible hinges to connect an anti-albumin Nb with two Nb14 domains. This construct was cloned in the pAOXZalfa vector, containing the α-mating factor pre-pro-signal sequence as a signal sequence, for the production of Nb proteins in yeast. (c) Affinity of Nb14, Nb14_NbAlb and Nb14_NbAlb_Nb14 (black) and their control Nb counterparts (gray) for mMMP8_CD was determined by ELISA (KD Nb14, 0.24 nmol/l; KD Nb14_NbAlb, 0.1 nmol/l; Nb14_NbAlb_Nb14, 0.016 nmol/l). (d) ELISA was performed to determine binding of the Nbs for mMMP8_FL (black) and results in KD values of 1.69, 0.63, and 0.057 nmol/l for Nb14, Nb14_NbAlb and Nb14_NbAlb_Nb14, respectively. The affinity of all Nbs was compared to mMMP8_CD in the same test (gray). (e) Binding capacity of all Nb conjugates for hMMP8_CD (gray) compared to mMMP8_CD (black) gave KD values of 158.4, 40.4, and 0.158 nmol/l for Nb14, Nb14_NbAlb and Nb14_NbAlb_Nb14, respectively. (n = 2) (f) Binding for albumin was determined via ELISA with Nb14 and Nbctrl as negative controls. Affinity of the monovalent NbAlb and the modified Nbs gives the following KD values: NbAlb, 0.32; Nb14_NbAlb, 8.14 nmol/l; Nb14_NbAlb_Nb14, 1.48 nmol/l; Nbctrl_NbAlb, 39.61 nmol/l; NbAlb_Nbctrl_Nbctrl, 2.013 nmol/l. (g,h) Binding affinities of the bispecific (n = 2) (g) and trispecific Nb14 (h) for mMMP8_CD were determined with surface plasmon resonance (SPR, Biacore). SPR analysis shows the on-rate, when the Nb binds the chip, in the first part of the graph, while the second phase represents the off-rate, when the Nb dissociates from its substrate (arrows). The full line shows the actual measurement, while the dotted line depicts the best theoretical fit. The best fit to determine KD values for Nb14_NbAlb is the two-state binding curve, while the best fit for Nb14_NbAlb_Nb14 is the bivalent binding model. This bivalent binding model describes the interaction of a monovalent ligand with a molecule carrying two identical and independent binding sites (KD Nb14_NbAlb, 240 nmol/l; KD Nb14_NbAlb_Nb14, 3.7 nmol/l). CD, catalytic domain; FL, full-length; h, human; KD, binding affinity constant; m, mouse; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; Nb, Nanobody; SPR, surface plasmon resonance; T1/2, half-life.