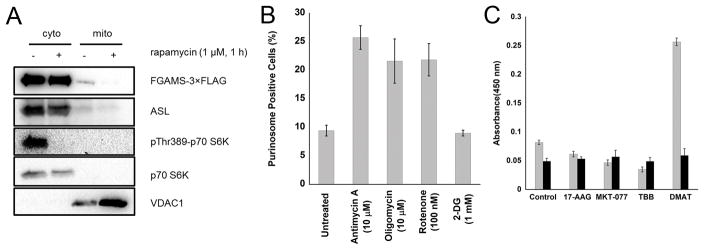
Fig. 4.
mTOR affects colocalization and functional links between purinosomes and mitochondria. (A) The percent of purinosome containing cells (determined from at least 100 cells) as a function of mitochondrial metabolism modulators in the absence (gray) and presence (black) of 100 nM rapamycin. Values reflect the mean ± standard deviation, N=3. (B) The percentage of purinosomes colocalized with mitochondria (black squares) as a function of increasing rapamycin concentration (10–1000 nM, 1 h). The results after randomization of the purinosome distribution are shown as gray crosses. The colocalization percentage is represented as the mean ± standard deviation, N=5 per condition.