Figure 4.
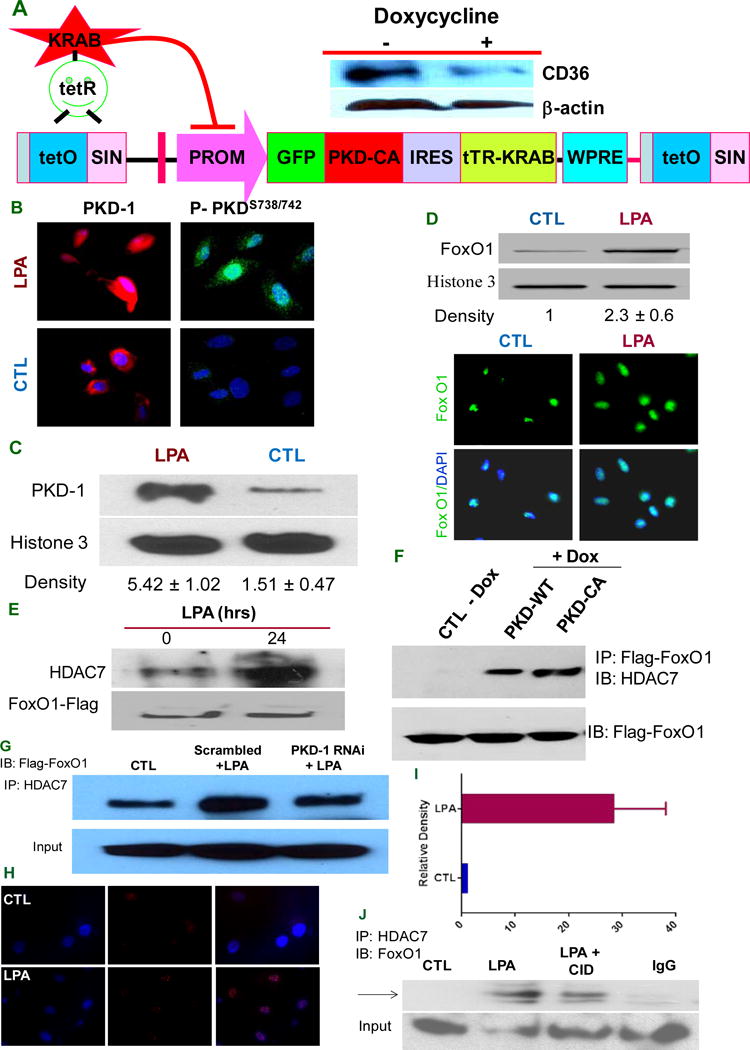
PKD-1 signals are required for HDAC7/FoxO1/interactions to regulate CD36 expression. A, PKD-CA expression inhibits CD36 expression in TAECs. A doxycycline-controllable single Lentiviral vector system containing pLVET-GFP: PKD-CA was established. TAECs were transduced with the vector and GFP positive clones were selected. Clone 3 cells were grown in the presence of 1 μg/ml doxycycline for 36 hrs and cell lysates were processed and subjected to Western blots. B, PKD-1 is translocated to the nucleus in response to LPA. HMVECs were exposed to LPA (5 μM) or vehicle for 24 hrs (left panels) or for 30 min (right panels) and incubated with anti-PKD-1 or anti-phospho-PKD-1 antibodies followed by Alexa Fluor® 2nd antibody. Images were obtained with a immunofluorescence microscopy or confocal microscopy. C, HMVECs were exposed to LPA (5 μM) for 24 hrs, the nuclear components were isolated and subjected to Western blots for total PKD-1 and histone 3 antibodies were used to determine nuclear protein loading (left panel). The relative PKD-1 level was determined by densitometry for triplicate experiments (right panel). D, FoxO1 level increases in the nucleus with LPA exposure. After LPA (10 μM) treatment for 24 hrs, ECs were subjected to immunofluorescence microscopy using anti-FoxO1 antibody (lower panel). In some studies nuclear components were isolated from the cells and subjected to Western blots for FoxO1 protein expression and relative density was calculated from triplicate experiments (upper panel). E, LPA promotes HDAC7-FoxO1 interaction. HMVECs were transfected with FoxO1-flag for 36 hrs and then exposed to LPA (5 μM) for 18 hrs. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with HDAC7 antibody and re-probed with anti-Flag antibody. Total cell lysate was subjected to Western blots for Flag-tag. F, Overexpressing PKD-1 increases HDAC7 interaction with FoxO1. TAECs transduced with pLVET-GFP: PKD1-WT or pLVET-GFP: PKD1-CA plasmids were co-transfected with FoxO1-Flag in the absence or presence of doxycycline (1 μg/ml) for 36 hrs. Cell lysates were collected and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, followed by Western blot analyses using anti-HDAC7 or anti-Flag antibody. G, PKD-1 is required for HDAC7-FoxO1 interactions. HMVECs transfected with scrambled RNAi plasmids (Scramble), or pSUPER PKD-1 RNAi and co-transfected with FoxO1 for 36 hrs were treated with LPA (5 μM) for 18 hrs and analyzed by Co-IP for FoxO1-HDAC7 interactions as in panel E. Representative results are shown in the figure. H, LPA exposure promotes interaction of endogenous HDAC7 and FoxO1 in the nucleus of HMVEC-C. In response to LPA (10 μM), there was a significant increase in the HDAC7-FoxO1 interaction in early passages of HMVEC-C (P3) detected as bright red dots in the cell nuclei by fluorescence microscopy using the Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA). I, Increased relative density of red fluorescent dots in the PLA indicating HDAC7-FoxO1 interactions in HMVEC-C exposed to LPA (10 μM). J, LPA-induced HDAC7-FoxO1 interaction was partially attenuated by PKD inhibitor. HMVEC-C (P3) wasexposed to LPA (10 μM), LPA (10 μM) plus a selective PKD inhibitor CID755673 (25 μM) or buffer control and the nuclei were isolated and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HDAC7 followed by immunoblot with anti-FoxO1 to detect endogenous interactions.
