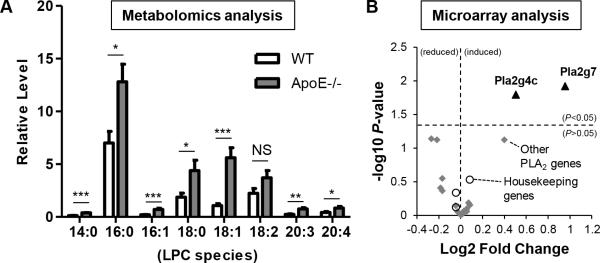
Figure 1. Aortic lysophoshatidylcholine (LPC) species are induced during early atherogenesis in mice.
Eight-week old wild-type (WT) mice and apolipoprotein E knockout (ApoE−/−) mice were fed with high-fat diet for 3 weeks before they were sacrificed. Aortas were collected from these mice for metabolomics analysis (A) and microarray analysis (B). A. Aortic LPC species were induced during early atherosclerosis. Relative changes of aortic LPC between WT and ApoE−/− were shown (n=8 per group). B. LPC-generating enzymes, including Pla2g4c and Pla2g7, were induced in the aortas during early atherosclerosis. Volcano plot was presented which showed fold change and statistical P value of expression changes of phospholipase A2 superfamily members and 3 housekeeping genes (Actb, Gapdh, and Nono) between ApoE−/− mice and WT mice (n=5 per group; solid triangle, significantly increased PLA2 genes; grey diamond, unchanged PLA2 genes; empty circle, control housekeeping genes). For all panels, values represent mean ± SEM. NS, not significant; *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001. WT, wild-type; ApoE−/−, apolipoprotein E deficient.