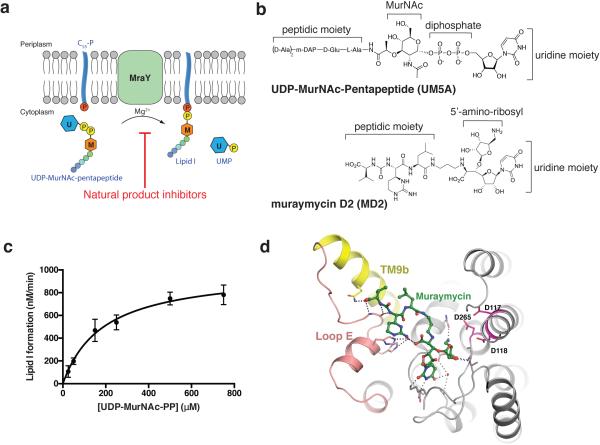
Extended Figure 1.
MraY catalyzes the formation of Lipid I and binds MD2. a, Scheme of the reaction catalyzed by MraY. The U-labeled blue hexagon represents uridine and the M-labeled orange hexagon represents MurNAc. The phosphates associated with the lipid carrier C55-P are shown as red circles, and the phosphates from the substrate, UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide (UM5A), are shown as yellow circles. b, Chemical structures of the substrate, UM5A (top) and the inhibitor MD2 (bottom). c, Michaelis-Menten kinetic characterization of MraYAA translocase activity. The reaction monitored is the MraYAA-catalyzed transfer of [14C]phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide from [14C]UM5A to C55-P, forming [14C]Lipid I. The enzymatic parameters measured are as follows: KM = 190 ± 60 μM, kcat = 20 ± 2 min−1, kcat/KM = 0.11 ± 0.3 μM−1 min−1. Data are shown as means of three technical replicates ± s.e.m. d, MD2 (green) in complex with MraYAA. The distances between MD2 and the three catalytic acidic residues D117, D118 and D265 (magenta) are all greater than 4.5 Å.