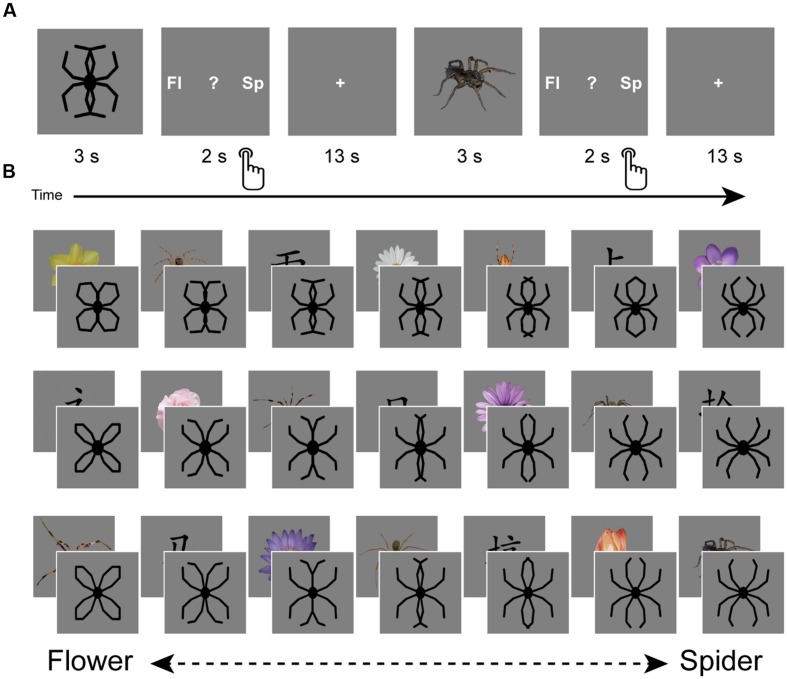
FIGURE 1.
Design. The experiment consisted of one session of fMRI scanning during which a generalization task was performed (A). This task consisted of the presentation of schematic flowers morphing to spiders (generously provided by Kolassa et al., 2007), intermitted by pictures of spiders, flowers and Chinese characters. Participants had to indicate whether they saw a spider (‘sp’), a flower (‘fl’) or none of the two (‘?’). Response buttons were counterbalanced over participants. Three variations existed of this flower-spider continuum (B). Each variation was presented once, but the fixed order of stimulus presentation (counterbalanced over participants) was designed in such a way that priming effects could be averaged out: each step of the continuum was once preceded by a flower, once by a spider and once by a Chinese character. Images are not to scale.