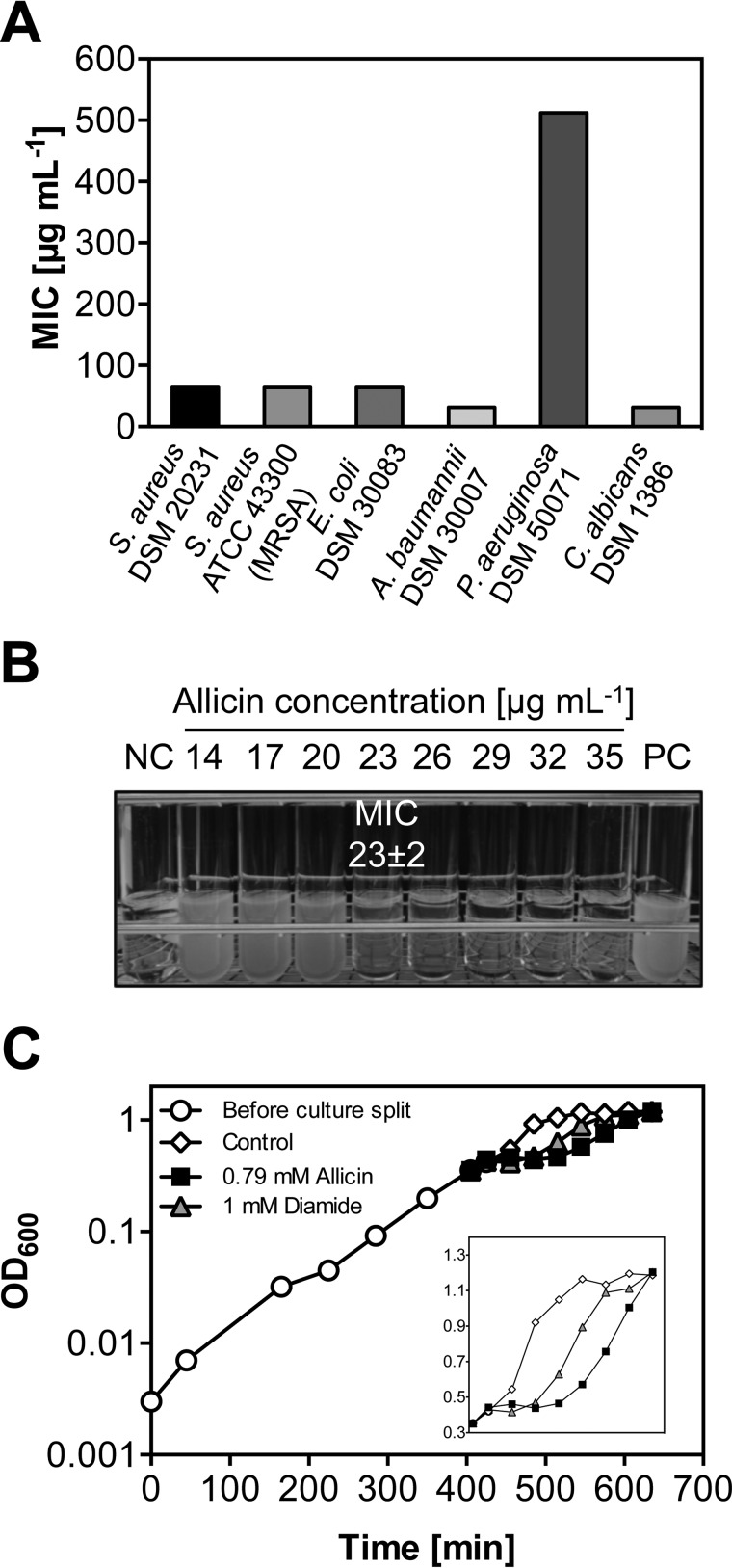
FIGURE 2.
Allicin inhibits growth of E. coli and other microorganisms. A, MICs of allicin against pathogenic microorganisms tested according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute standards in a microtiter plate-based assay using rich medium. B, a more precise determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration of allicin against E. coli MG1655 in MOPS minimal medium. Overnight cultures did not show visible growth at allicin concentrations above 23 μg ml−1. Negative control (NC), not inoculated; positive control (PC), without allicin. C, addition of 0.79 mm allicin (128 μg ml−1) or 1 mm diamide to midlogarithmic E. coli MG1655 (black arrow) causes a growth arrest. Cultures resumed growth after 60 and 90 min, respectively.