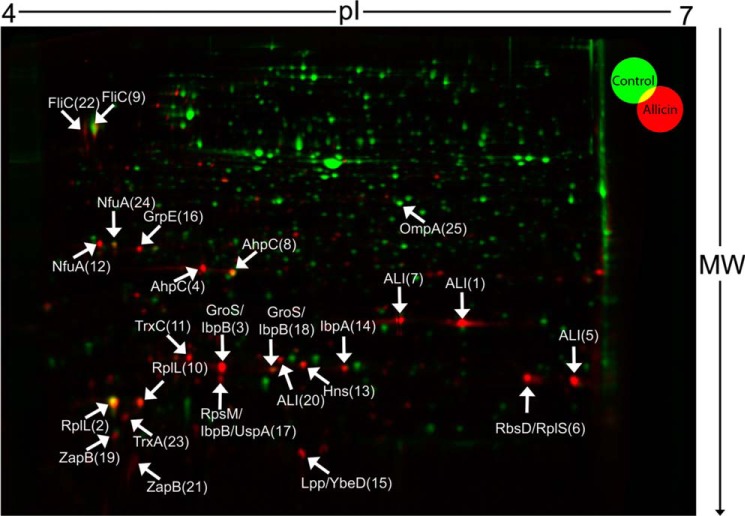
FIGURE 5.
Allicin treatment induces heat shock and oxidative stress response in E. coli. Newly synthesized proteins of untreated (green) and allicin-treated (red) E. coli cultures were analyzed by [35S]methionine labeling prior to separation by two-dimensional PAGE and detection of spots using a phosphor screen. [35S]Methionine incorporation was found to be 44% of the control in the allicin-treated culture, suggesting a decreased protein synthesis upon allicin treatment. An overlay of gel images was performed to identify proteins expressed in response to allicin treatment. The 25 spots with the highest synthesis rates in allicin-treated E. coli were cut from non-radioactive gels, trypsin-digested, and analyzed by mass spectrometry. The numbers behind protein names represent spot numbers in Table 1. ALI indicates allicin-induced spots that could not be identified by mass spectrometry. Shown are representative gels from three individual biological replicates.