FIGURE 4.
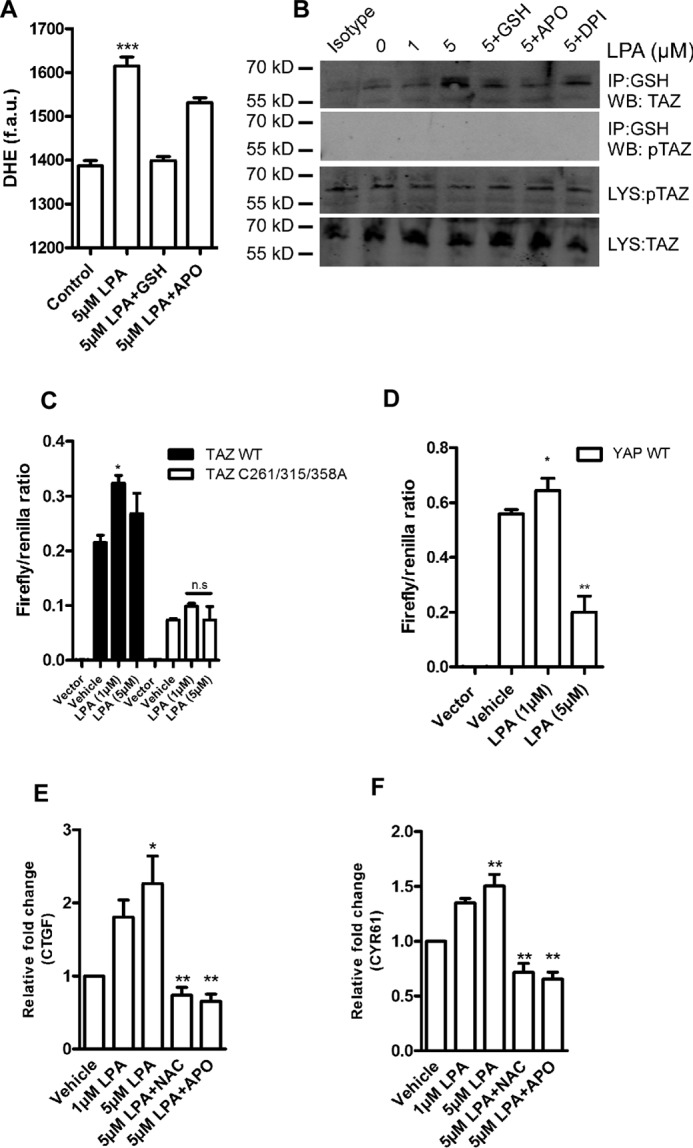
LPA induces TAZ S-glutathionylation. A, HEK 293T cells were treated with 5 μm LPA for 1 h. After treatment, cells were loaded with DHE, and superoxide elevation was quantified as fluorescence arbitrary units (f.a.u.) in a fluorescence plate reader. APO, apocynin. B, HEK 293T transiently expressing FLAG.TAZ were challenged with 1 and 5 μm LPA for 1 h. After IP with anti-GSH antibody, Western blotting (WB) analyses revealed that wild-type TAZ undergoes S-glutathionylation in a dose-dependent manner, which was inhibited with pretreatment of antioxidants and the pan NOX inhibitor apocynin or diphenyliodonium (DPI). Mouse IgG IP (isotype) is shown as a control. C, TEAD reporter activity of TAZ wild-type and the cysteine triple mutant 6 h following LPA treatment. D, TEAD reporter activity of YAP wild-type 6 h following LPA exposure. E and F, HEK 293T cells transiently expressing FLAG.TAZ were challenged with 1 or 5 μm LPA for 6 h. TAZ target gene CTGF and CYR61 levels were quantified by qPCR. LPA induces TAZ-mediated CTGF and CYR61 expression, which is attenuated with pretreatment with 2 mm N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and 10 μm apocynin. Data are mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant).
