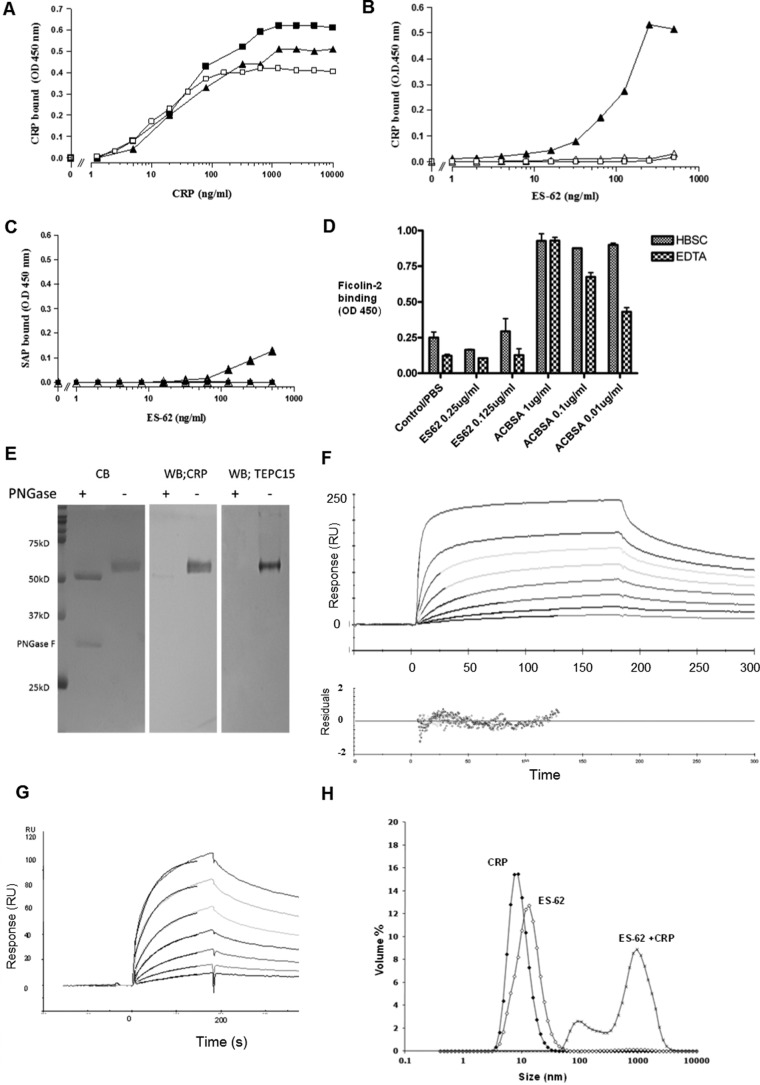
FIGURE 1.
High-avidity binding of C-reactive protein to ES-62 is calcium-dependent and can be inhibited by PCh. A, dose response of binding of purified CRP to immobilized ES-62 (2.0 μg/ml, ■), PCh-BSA (0.5 μg/ml, ▴), or CWPS (5 μg/ml, □) on microtiter plates. Various concentrations of CRP were offered, and binding of CRP was detected using polyclonal anti-human CRP-HRP. OD, optical density. B, CRP binding from ES-62 is calcium-dependent and can be inhibited by PCh. Various concentrations of ES-62 were coated onto microtiter plates, and normal serum diluted 1 in 50 to give a final CRP concentration of 50 ng/ml was added. Binding of CRP was detected with the anti-native human CRP monoclonal antibody 2C10 and anti-mouse IgG HRP and 1,1,3,3 tetramethylbenzidine substrate (optical density, 450 nm). Serum was diluted in HBS containing 1 mm CaCl2 (▴), HBS with 10 mm EDTA (▵), or HBS with 1 mm CaCl2 and 50 mm phosphorylcholine (□). C, SAP provided in serum diluted 1 in 50 binds weakly to ES-62 (▴) but not PCh-BSA-coated plates (■). SAP was determined using monoclonal anti-SAP and anti-mouse IgG HRP. Controls show binding to ES-62 in the presence of EDTA (▵). D, plates were coated with ES-62 or the positive control acetylated BSA (ACBSA) at various concentrations, serum was added in the presence or absence of calcium, and binding was detected with biotinylated anti-ficolin 2 and streptavidin HRP. Data are mean ± S.E. of triplicates. E, ligand blotting of ES-62 following SDS-PAGE demonstrates binding of C-reactive protein to PCh attached to N-linked glycan. Left panel, ES-62 or ES-62 deglycosylated with PNGase stained directly with Coomassie Blue (CB). Center panel, ES-62 was transferred to PVDF, and CRP binding in TBSC was detected with anti-CRP and anti-mouse-alkaline phosphatase. Right panel, as for the center panel, but PCh was detected with anti-PCh myeloma protein, TEPC15. WB, Western blotting. F, surface plasmon resonance analysis of interaction. ES-62 was immobilized, and CRP was offered at concentrations of 10, 2.5, 1.25, 0.62, 0.3, 0.16, 0.08, and 0.04 μg/ml. Langmuir 1:1 analysis was performed. Residuals from the association analysis are shown below. RU, response unit. G, surface plasmon resonance analysis of ES-62 (12.5, 6.25, 3, 1.6, 0.8, 0.4, and 0.2 μg/ml) binding to biotinylated CRP immobilized on a streptavidin surface. The superimposed lines show modeled fit. H, CRP and ES-62 form large complexes in fluid phase. The size of the complex was determined using light scattering 5 min after mixing for 50 μg/ml CRP and 65 μg/ml ES-62 in HBS in the presence of 1 mm CaCl2.