Figure 9.
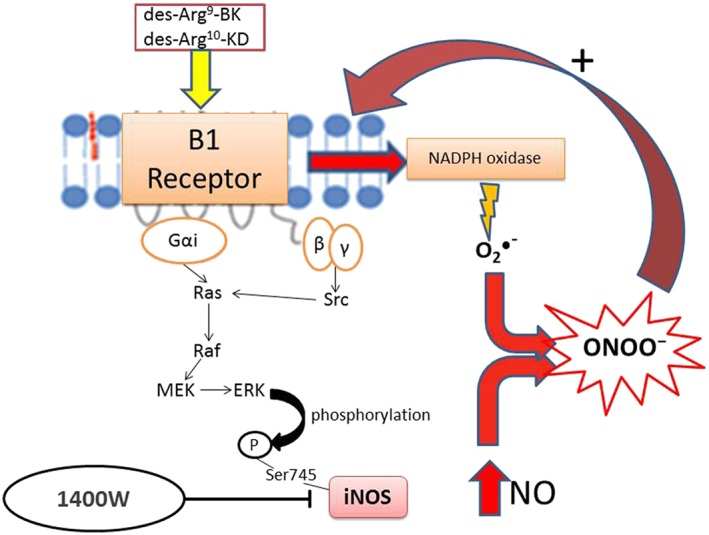
Schematic diagram of the signalling pathway activated by B1 receptor agonists leading to the formation of ONOO¯ upon post‐translational activation of iNOS and NADPH oxidase. Activation of the B1 receptor through Gαi and βγ‐dependent activation of Src, Ras, Raf and MEK leads to ERK‐dependent phosphorylation of iNOS on Ser745 that causes high NO output (Brovkovych et al., 2011). Simultaneously, B1 receptor agonists can activate NADPH oxidase to generate O2 ●¯ (Dias et al., 2010) that can rapidly react with NO to form ONOO¯. The latter exerts a positive feedback loop to enhance the expression of B1 receptors. Blockade of iNOS with 1400W prevents this vicious cycle and the pro‐inflammatory effects of B1 receptors.
