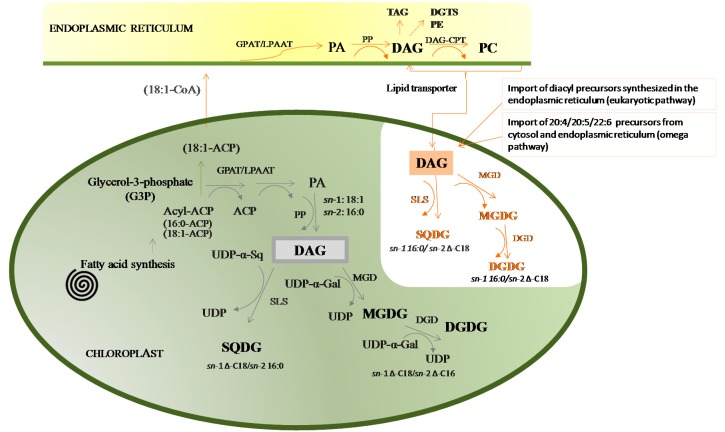
Figure 2.
Simplified diagram of the main pathways involving the biosynthesis of glycerolipids in microalgae. The set of reactions occurring within the chloroplast are termed the chloroplastic or ‘‘prokaryotic” pathway and those that involve glycerolipid synthesis in the ER (endoplasmic reticulum) and subsequent transfer to the chloroplast constitute the endoplasmic or “eukaryotic” pathway. Orange arrows refer to the biosynthetic pathway of transport of ER-derived glycerolipids to chloroplasts. Enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of glycolipids are shown. ACP, acyl carrier protein; PA, phosphatidic acid; DAG, diacylglycerol; PC, phosphatidylcholine; MGD, MGDG syntases; DGD, DGDG synthases; UDP, uridine diphosphate galactose intermediate in the production of polysaccharides (-Gal galactose, -Sq sulfoquinovose); GPAT, glycerol-3-phosphatase acyltransferase; LPAAT, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase; PA, phosphatidic acid; PP, phosphatidate phosphatase; DAG-CPT, diacylglycerol synthetase-choline: diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase; SLS, sulfolipid synthase; SQDG, sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; DGTS, diacylglyceryl trimethylhomo-serine; TAG, triacylglycerol; ∆, degree of unsaturation ranging from 1 to 4 double bonds.