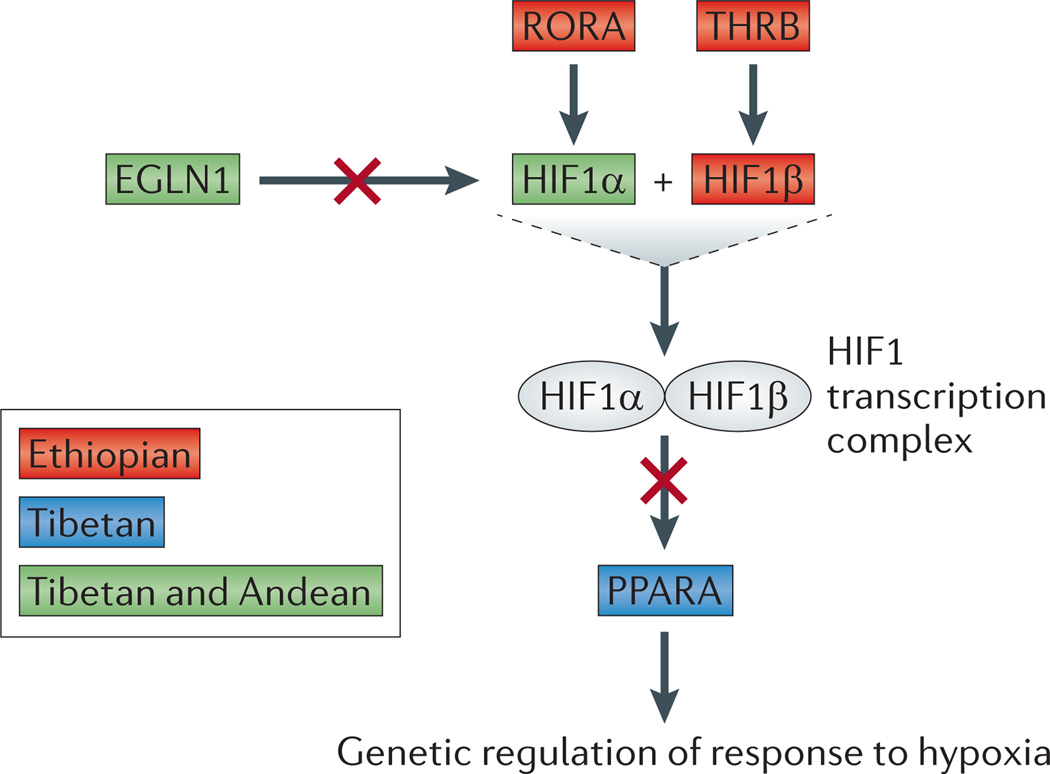
Figure 2. An abridged hypoxia-inducible factor 1 pathway.
Distinct genes in the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF1) pathway are implicated in adaptation in different high-altitude populations (living at altitudes >2,500 metres above sea level) owing to convergent adaptation. Each gene interaction involving a candidate adaptive gene for high altitude is shown in relation to the HIF1 pathway. Genes that have been implicated as candidate adaptive genes in high-altitude Ethiopian populations78,79, high-altitude Tibetan populations33,49,76,77, and high-altitude Tibetan and Andean populations74 are indicated. HIF1α (also known as EPAS1) and HIF1β (also known as ARNT2) form a heterodimer known as the HIF1 transcription complex. Thyroid hormone receptor-β (THRB) is required for the expression of the HIF1 transcription complex, RAR-related orphan receptor A (RORA) induces transcription of HIF1α, egl nine homologue 1(EGLN1) is involved in the degradation of the HIF1 transcription complex, and the HIF1 transcription complex inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARA) expression.