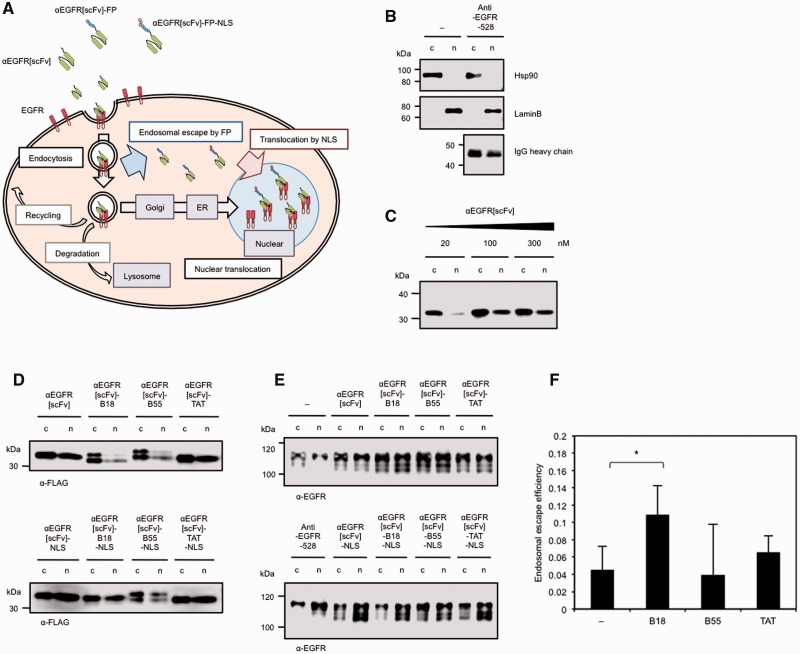
Fig. 3.
Estimating the endosomal escape efficiency of FP-fused αEGFR scFv proteins by utilizing an NLS. (A) Scheme for the intracellular trafficking of αEGFR[scFv], FP-fused αEGFR[scFv] (αEGFR[scFv]-FP) and FP-NLS-fused αEGFR[scFv] (αEGFR[scFv]-FP-NLS). (B) Confirmation of fractionated lysates and of the nuclear translocation of αEGFR-528 IgG as a ligand of EGFR. Immunoblotting was performed with anti-Hsp90, anti-LaminB and anti-mouse IgGs on fractionated lysates from A431 cells treated with 2 µg/ml of anti-EGFR-528 IgG for 4 h. The electrophoresis ratio between the non-nuclear fraction) (c) and the nuclear fraction (n) was 1:2. (C) Confirmation of the nuclear translocation of αEGFR[scFv] as a ligand of EGFR. Immunoblotting was performed with an anti-FLAG IgG on fractionated lysate from A431 cells treated with 20–300 nM of αEGFR[scFv] for 4 h. The electrophoresis ratio of (c) and (n) was 1:4. (D and E) Immunoblots with anti-FLAG IgG (D) or an anti-EGFR IgG recognizing the intracellular domain of EGFR (E) on fractionated lysates from A431 cells treated with 300 nM of each αEGFR[scFv] fusion protein or with 2 µg/ml of αEGFR-528 IgG for 4 h. The electrophoresis ratio between (c) and (n) was 1:4 (D) or 1:2 (E). (F) The endosomal escape efficiency of each αEGFR[scFv] fusion protein as estimated by the difference between the proportions of FP-fused αEGFR[scFv] proteins and the proportion of FP-NLS-fused αEGFR[scFv] proteins in the nuclear fraction. The ‘−’ sample indicates αEGFR[scFv] without a fused FP. N = 5. Mean ± SD. *P < 0.05.