Figure 1.
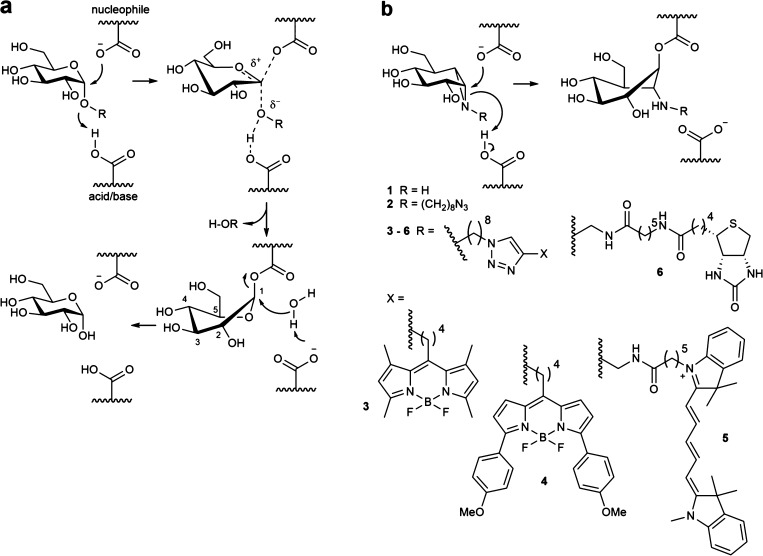
The mechanism of action of retaining α-glucosidases allows the development of activity-based probes. (a) Koshland double-displacement mechanism employed by retaining α-glucosidases. (b) α-Glucose-configured N-alkyl cyclophellitol aziridines as mechanism-based irreversible retaining α-glucosidase inhibitors (1, 2) and probes (3–6).