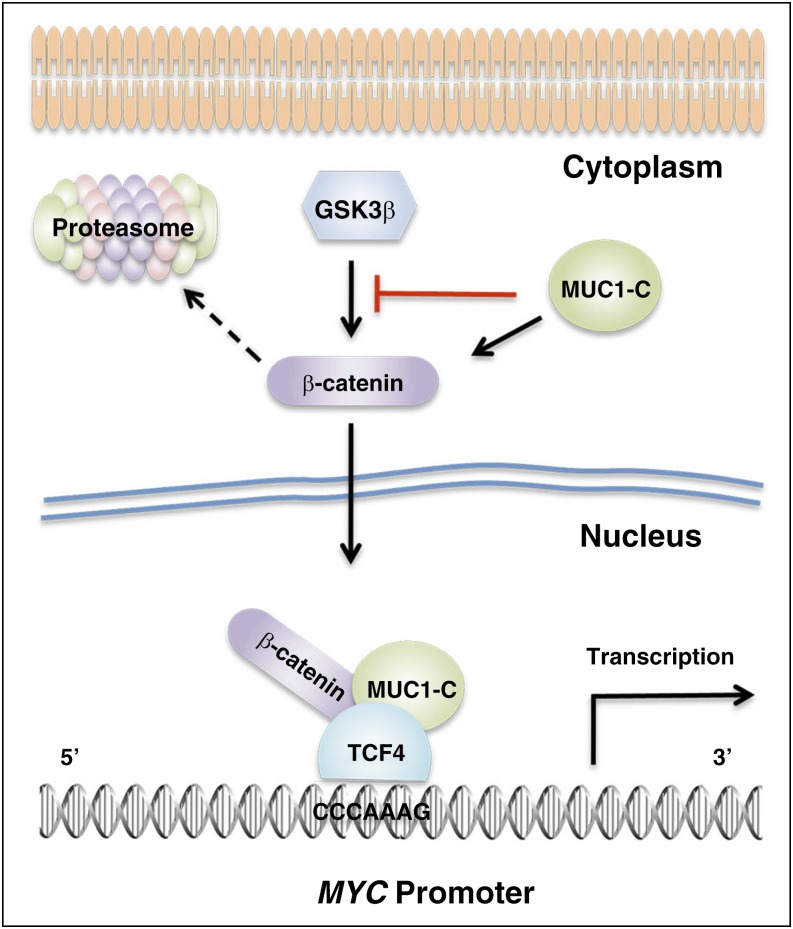
Figure 7.
Schema of the proposed MUC1-C–mediated induction of MYC expression in MM cells. MUC1-C is aberrantly expressed in MM cell lines and primary MM cells.13-18 The MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain binds directly to β-catenin and inhibits β-catenin degradation.22 The MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain also functions as a substrate for GSK3β and blocks GSK3β-mediated β-catenin phosphorylation.22,23 In turn, the upregulation of both MUC1-C and β-catenin promotes the formation of MUC1-C/β-catenin complexes that interact with TCF4 on the MYC promoter and drive MYC transcription. In concert with this model, targeting MUC1-C decreases β-catenin levels and the activation of MYC expression.