Figure 1.
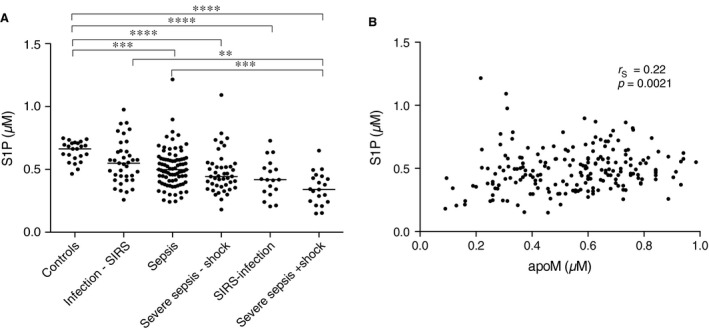
S1P decreases in human sepsis. Human adult patients admitted to the emergency department with suspicion of infection were enrolled in the study based on the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)‐criteria. Plasma was collected from patients with severe sepsis with shock (n = 20), severe sepsis without shock (n = 44), sepsis (n = 83), infections without SIRS (n = 37), SIRS without infection (n = 18) and healthy controls (n = 23). Plasma S1P was quantified by LC‐MS/MS (A) and correlated with plasma apoM (B). Statistical analysis was performed with a Kruskal–Wallis test *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, r s = Spearman's correlation coefficient.
