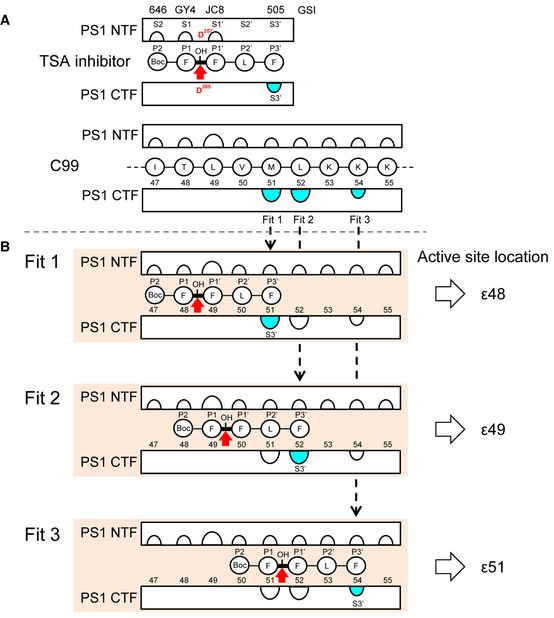
Comparison of the C99 interaction sites with the known interaction sites of transition state analog GSIs (Li
et al,
2000b; Shelton
et al,
2009) suggests that the binding site of these GSIs locates at the ε‐cleavage sites of C99. Using differently placed photoreactive benzophenone moieties in the FFLF peptide‐based L‐685,458 GSI derivatives L‐852,646 (646), GY4, JC8, and L‐852,505 (505), the S2‐S1′ pockets were previously located to the PS1 NTF (Li
et al,
2000b; Shelton
et al,
2009). In addition, the S3′ pocket could almost exclusively be located to the PS1 CTF by GSI 505 (Li
et al,
2000b; Shelton
et al,
2009). Preferential location of the S3′ pocket to the PS1 CTF was also observed for the related GSI III‐63 (Kornilova
et al,
2005). As determined here, the only sites of C99 that crosslinked to the PS1 CTF were residues M51, L52, and K54.