Figure 2.
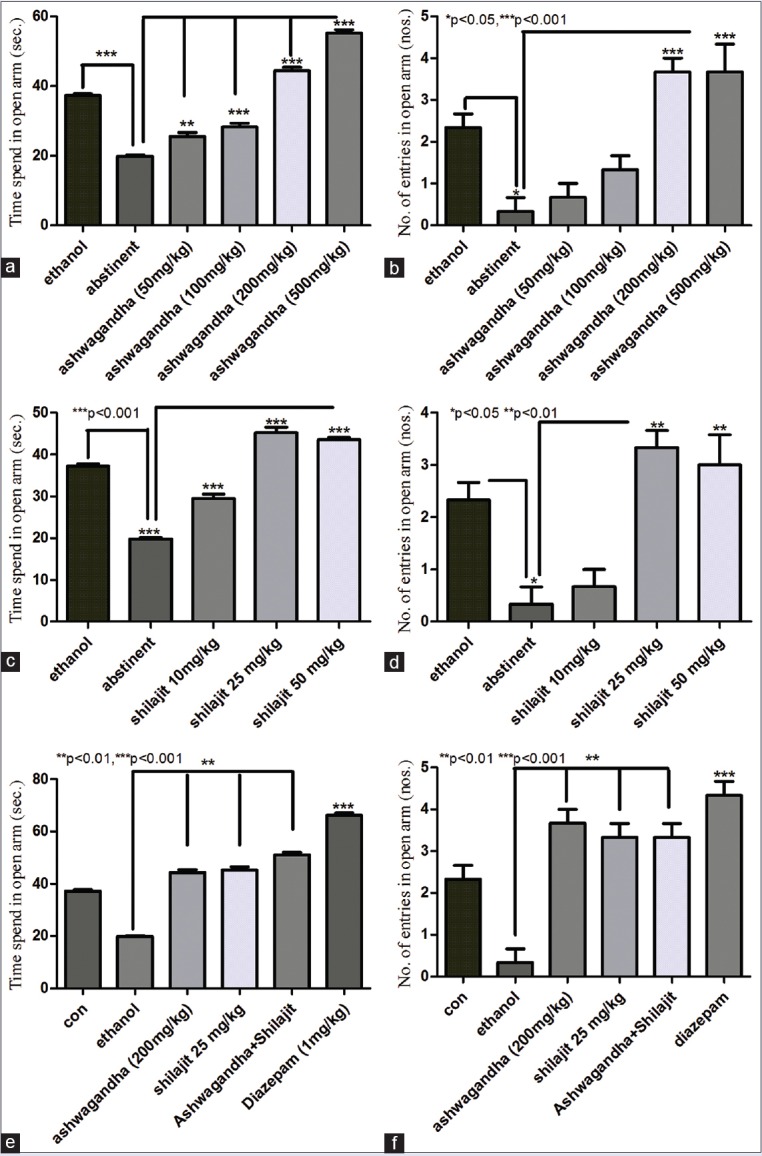
Effect of ashwagandha and shilajit on ethanol withdrawal anxiety using elevated plus maze. (a) Ethanol abstinence significantly decreased (P < 0.001) time spend in open arm compared to ethanol-treated animals. Ashwagandha treatment to abstinent animals significantly (50 mg/kg P < 0.01 and 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg, 500 mg/kg P < 0.001) increased the time spend in open arm compared to ethanol abstinent animals. (b) Ethanol abstinence significantly decreased (P < 0.001) the number of entries in open arm compared to animals on ethanol. Ashwagandha treatment (200 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg) significantly (P < 0.001) increased the number of open arm entries compared to abstinent animals. (c) Ethanol abstinence significantly decreased (P < 0.001) time spend in open arm compared to ethanol-treated animals. Shilajit treatment to abstinent animals significantly (10 mg/kg, 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg P < 0.001) increased the time spend in open arm compared to ethanol abstinent animals. (d) Ethanol abstinence significantly decreased (P < 0.05) the number of entries in open arm compared to animals on ethanol. Shilajit treatment (25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg) significantly (P < 0.01) increased the number of open arm entries compared to abstinent animals. Values (e) Ashwagandha (200 mg/kg) and shilajit (25 mg/kg) together significantly increased (P < 0.01) the time spend in open arm compared to ethanol abstinent animals. However, this increase was comparable (P > 0.05) with ashwagandha (200 mg/kg) and shilajit (25 mg/kg) treatments alone. Diazepam also significantly increased time spend in open arm over ethanol abstinent and ethanol-treated groups (P < 0.001). (f) Ashwagandha (200 mg/kg) and shilajit (25 mg/kg) together significantly increased (P < 0.01) the number of entries into the open arm when compared with ethanol abstinent animals. However, this increase was comparable (P > 0.05) with ashwagandha (200 mg/kg) and shilajit (25 mg/kg) treatments alone. Diazepam also significantly increased the number of open arm entries over ethanol abstinent and ethanol-treated groups (P < 0.001). Values represent mean ± standard error of the mean n = 7
