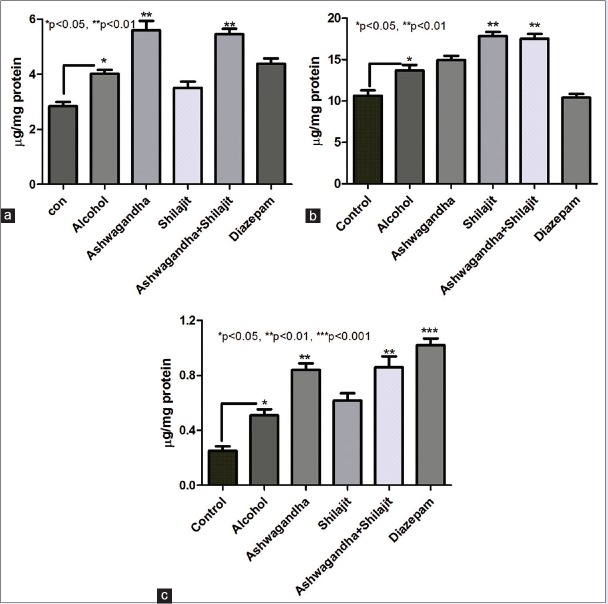
Figure 4.
Effect of ashwagandha and shilajit on central nervous system neurotransmitter levels. (a) Changes in serotonin levels before and after treatment. Ashwagandha (500 mg/kg) as well as combined ashwagandha and shilajit treatment (day 21–30) lead to significant increase (P < 0.01) increase in corticohippocampal serotonin compared to untreated animals on ethanol (30 days). However, treatment with shilajit (50 mg/kg) alone or diazepam failed to increase serotonin levels compared to alcohol treated group. (b) Changes in dopamine levels before and after treatment. Shilajit (50 mg/kg) as well as ashwagandha and shilajit combination treatment (day 21–30) led to significant increase (P < 0.01) in corticohippocampal dopamine compared to untreated animals on ethanol (30 days). However, treatment with ashwagandha (500 mg/kg) alone or diazepam failed to increase serotonin levels compared to alcohol treated group. (c) Changes in gamma-aminobutyric acid levels before and after treatment. Ashwagandha (500 mg/kg) as well as combined ashwagandha and shilajit treatment (day 21–30) led to significant increase (P < 0.01) increase in corticohippocampal gamma-aminobutyric acid levels compared to untreated animals on ethanol (30 days). However, treatment with shilajit (50 mg/kg) alone failed to increase serotonin levels compared to alcohol-treated group. Diazepam treatment also showed a significant increase (P < 0.001) increase in corticohippocampal gamma-aminobutyric acid levels. Values represent mean ± standard error of the mean n = 5