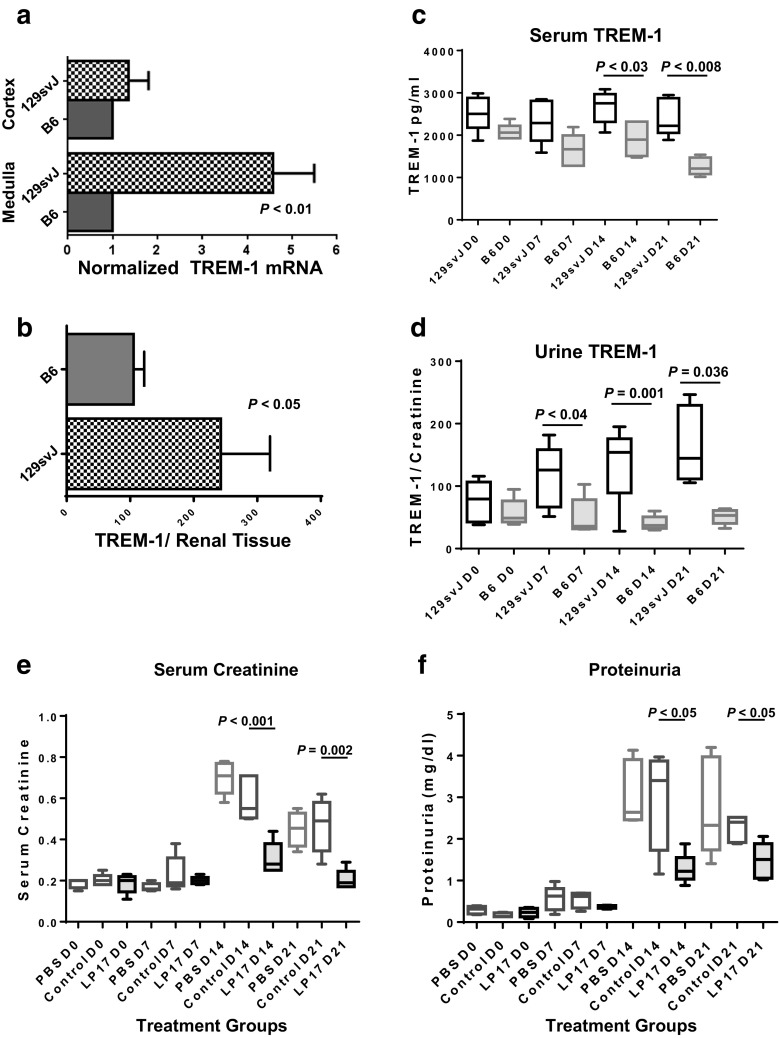
Fig. 1.
Elevated TREM-1 mRNA and protein expression in anti-GBM-induced nephritis. Anti-GBM was induced and 7 days later, the kidneys were examined for TREM-1 mRNA and protein. a TREM-1 mRNA levels were elevated in the renal medulla of 129/SvJ compared to B6 mice. b TREM-1 protein was detected by ELISA in renal eluates from 129/SvJ and control B6 mice. c Soluble TREM-1 levels were reduced in the serum of control B6 mice compared to the 129/SvJ mice on days 14 and 21 as a result of an actual decrease in soluble TREM-1 levels in B6 mice over the course of disease. d Soluble TREM-1 was significantly elevated in the urine of 129/SvJ compared to control B6 mice. Soluble TREM-1 levels were also elevated in the urine of 129/SvJ on day 21 compared to 129/SvJ on day 0 (P < 0.05). Urine soluble TREM-1 levels were normalized to creatinine. TREM-1 blockade inhibits anti-GBM disease in 129/SvJ mice. Anti-GBM-induced mice were randomly divided into three groups (n = 5 each) receiving (1) PBS, (2) control scrambled peptide, or (3) LP17 peptide. Mice received daily treatment with controls or LP17 peptide. e Serum creatinine levels were elevated on days 14–21 in mice receiving PBS or control peptide, but only slightly elevated in LP17-treated mice. f Proteinuria was observed in control mice, but not in LP17-treated mice through day 21. Statistical analysis was carried out by Mann-Whitney U tests to obtain the P values shown.