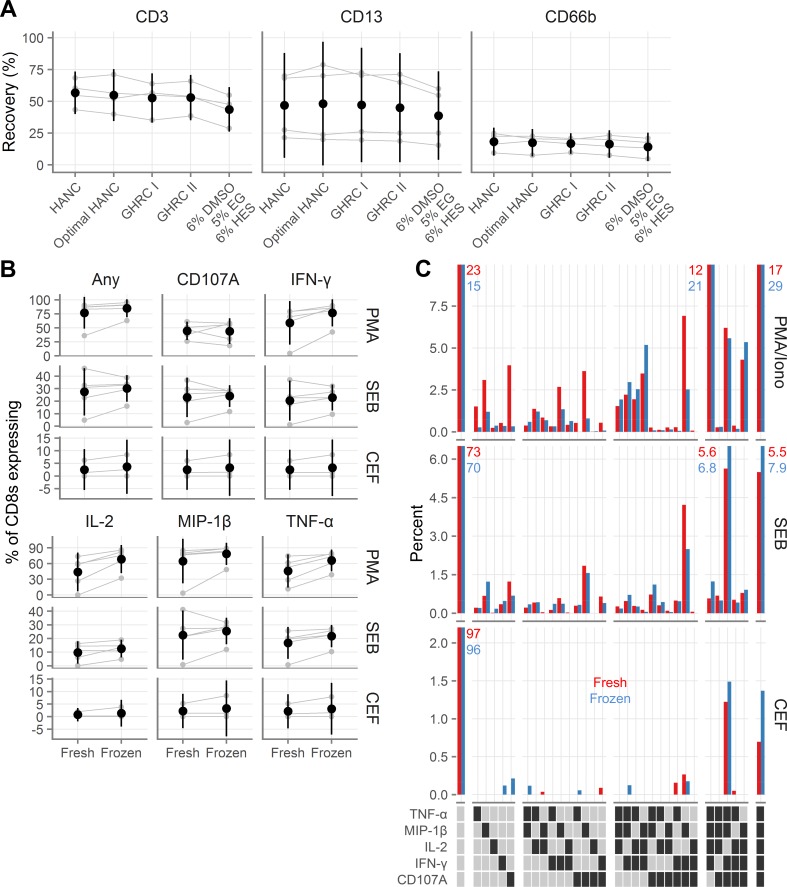
Fig 5. Recovery and functionality of colorectal cells after cryopreservation.
A, Recovery of colorectal T cells (indicated “CD3”), macrophages (indicated “CD13”), and neutrophils (indicated “CD66b”), after cryopreservation with several cryopreservation media. GHRC I [Global HIV Vaccine Research Cryorepository] is 10% DMSO alone and GHRC II is 5% DMSO with 6% hydroxyethyl starch, both in RPMI with 12.5% bovine serum albumin. HANC is 10% DMSO in FBS. HANC was processed according to procedure C and the others were processed with procedure B (see Table 1). B, Background-subtracted cytokine production from colorectal CD8 T cells fresh or after cryopreservation after stimulation with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA); staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB); or human cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus and influenza virus peptides (CEF). Gray symbols indicate the individual samples, with gray lines indicating pairing. Black symbols show the mean across all samples and black vertical lines show the 95% confidence interval of the mean. C, Polyfunctionality of colorectal CD8 cytokine responses to stimulation. Red bars indicate fresh samples and blue bars indicate samples tested after cryopreservation. Each bar corresponds to the percent of CD8 cells that expressed the indicated cytokines, averaged across the donors. Percentages are indicated explicitly for bars that exceed the axis limits of the graphs. In the legend, a dark square indicates presence of that cytokine and a light square its absence. White gaps divide the graphs and legends into groups expressing 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 cytokines.