Figure 1.
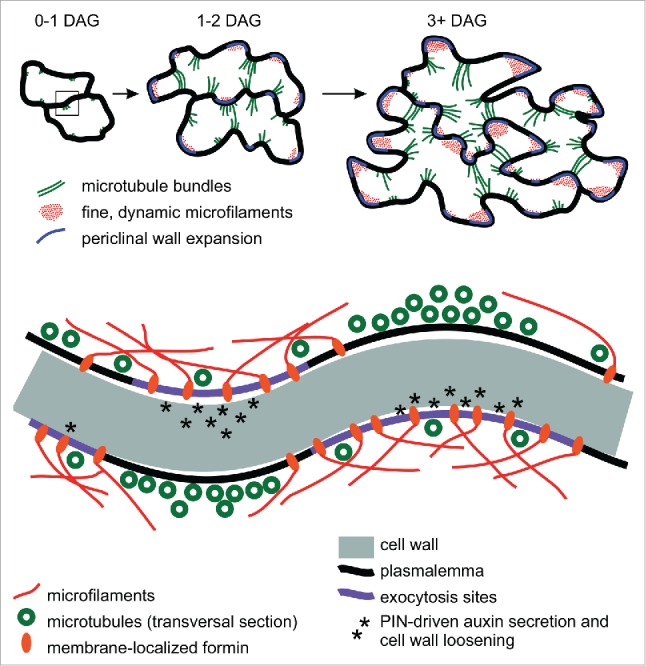
A model of the structural aspects of pavement cell shape specification. Top: temporal sequence of cytoskeletal rearrangements22 during early stages of pavement cell development.11 Bottom: close-up of a periclinal section of the interface of two neighboring cells at an early stage of pattern establishment (box in the top part of the figure). Membrane-anchored formins may contribute to the focusing of microtubule bundles to future indentations by restricting lateral mobility of cortical microtubules through nucleation of membrane-attached microfilaments, promoting assembly of cortically anchored actin cables.25 Unlike ARP2/3-nucleated actin arrays, these cables might form only a sparse meshwork, sufficient to prevent microtubule bundling but not interfering with exocytosis (compare ref. 21). At later stages, ARP2/3-mediated actin nucleation might take place on the existing formin-generated actin filaments, aiding actomyosin-driven vesicle delivery to expanding areas of the cell cortex. DAG - days after germination.
