Figure 2.
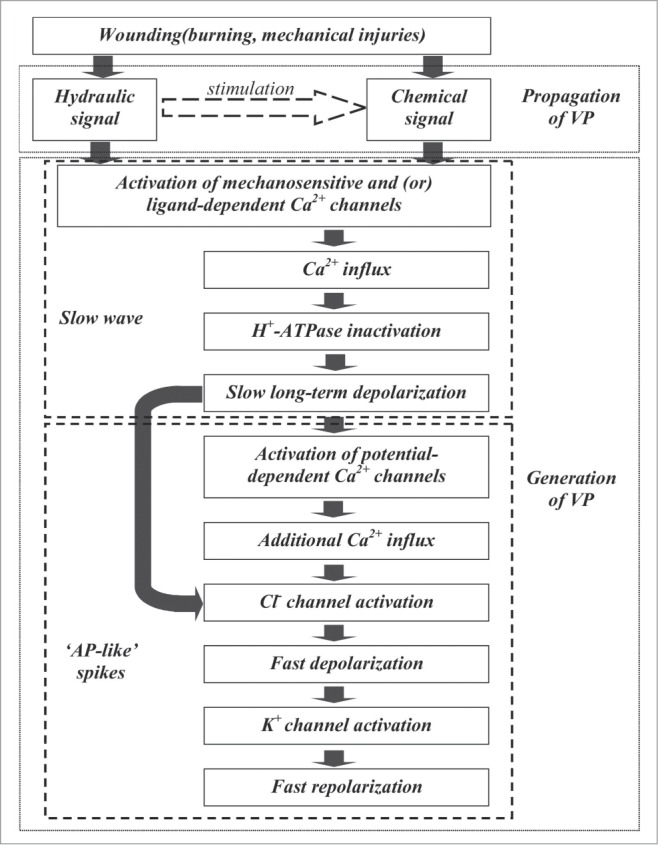
Hypothetical mechanism of VP generation and propagation. Propagation of chemical signal, hydraulic signal or combination of these signals (hydraulic dispersion and turbulent diffusion) activated ligand-dependent or mechano-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Ca2+ influx inactivates H+-ATPase and induces long-term depolarization. Depolarization to AP threshold activates potential-dependent Ca2+ channels. Additional Ca2+ influx and plasma membrane depolarization activate potential-dependent Cl− channels, and, later, K+-channels. As a result AP-like spike is formed.
