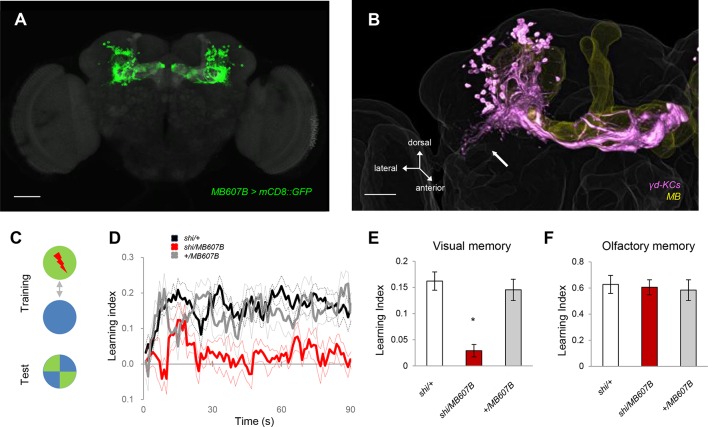
Figure 1. The γd KCs are required for visual memory.
(A) γd neurons labeled by MB607B-GAL4. (B) 3D reconstruction of γd neurons labeled by MB607B-GAL4 (purple) in the entire MB (yellow). Arrow indicates atypical dendritic protrusion of the γd neurons. Scale bars: 50 µm (A) and 20 µm (B). (C) Schematic diagram of color discrimination learning and test. (D) Average time courses of conditioned color avoidance in the test for flies with the blockade of the γd neurons with MB607B-GAL4 (red) and the parental controls (black and gray). (E) Pooled conditioned color avoidance. Blocking the γd neurons with MB607B-GAL4 impairs aversive color discrimination learning (one-way ANOVA, post-hoc pairwise comparison, p<0.05; n = 8–12). (F) The same Shits1 blockade of the γd neurons does not impair immediate aversive olfactory memory (one-way ANOVA, post-hoc pairwise comparison, p>0,05; n = 9–10). Throughout this study, bars and error bars display mean and SEM, respectively.