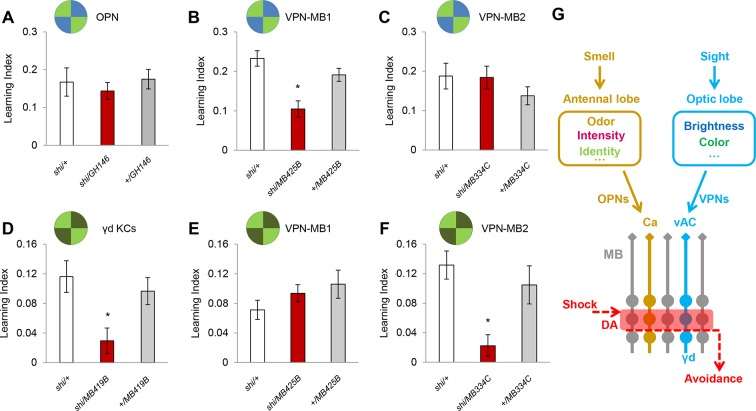
Figure 4. VPN-MB1 and VPN-MB2 convey distinct visual features.
(A) OPNs labeled by GH146-GAL4 are not required for visual color conditioning (one-way ANOVA, p>0.05), n = 8. (B–C) VPN-MB1 (MB425B-GAL4; B), but not VPN-MB2 (MB334C-GAL4; C), are required for color discrimination learning (one-way ANOVA, post-hoc pairwise comparison, p<0.01). n = 9–12. (D) γd neurons labeled by MB419B-GAL4 are required for green intensity learning (one-way ANOVA, post-hoc pairwise comparison, p<0.05), n = 9–11; these neurons are also required for color discrimination learning (Figure 1). (E–F) In contrast to the requirement in color discrimination learning, the blockade of VPN-MB2 (MB334C-GAL4; F), but not VPN-MB1 (MB425B-GAL4; E), significantly impaired intensity discrimination learning (one-way ANOVA, post-hoc pairwise comparison, p<0.05). n = 8–13. (G) Schematic of memory circuits in the MB. Visual and olfactory information is first processed in the optic lobe and antennal lobe, respectively. Components of sensory information (e.g. brightness and color) are separately processed there and conveyed to corresponding KC subtypes in the MB directly through distinct projection neurons Ca: calyx, vAC: ventral accessory calyx. These segregated representations of visual and olfactory information undergo the same dopaminergic (DA) valence modulation to operate acquired behavior (e.g. conditioned avoidance) via shared circuits.
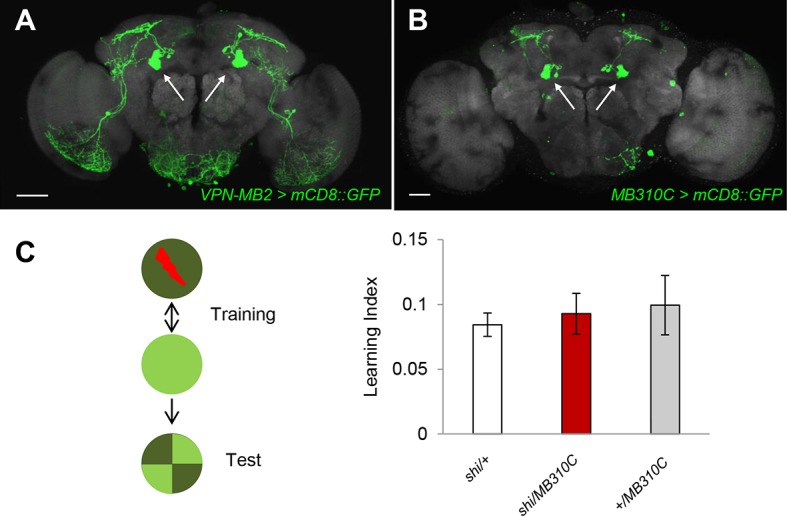
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. The blockade of similar VPNs without vAC connection does not impair color discrimination learning.
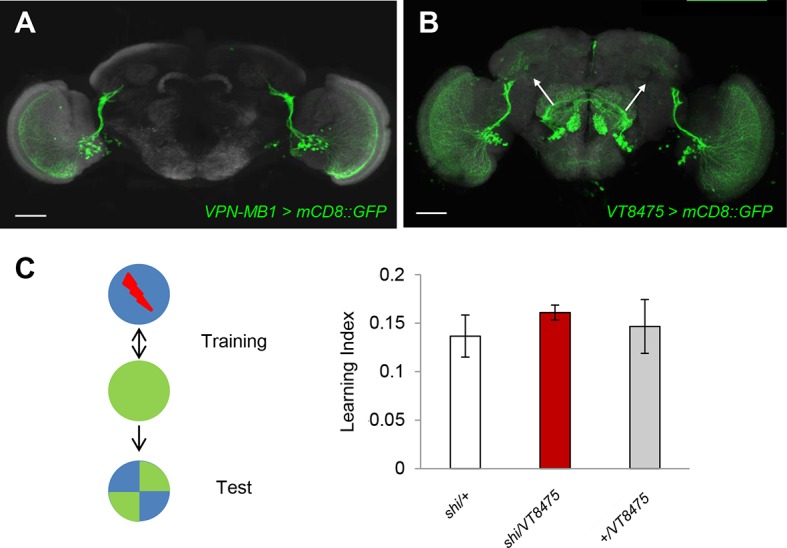
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. The blockade of MBON-a1 does not impair intensity discrimination learning.