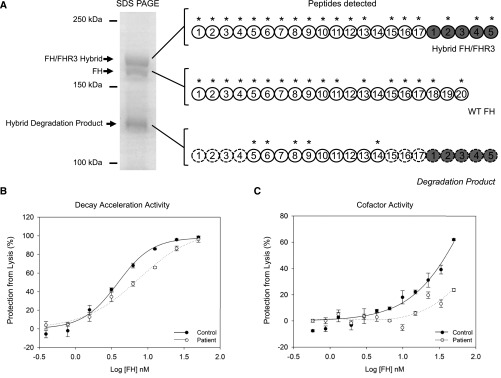
Figure 4.
Impaired cell surface co-factor and decay acceleration activity of hybrid FH/FHR3 hybrid protein. (A) Mass spectrometry of purified proteins. The FH, FH/FHR3 hybrid, and degradation product were purified using affinity chromatography with an OX24 column. These FH species were separated by 6% SDS-PAGE, stained using Coomassie, cut from the gel (left panel), and submitted for trypsin digest and mass spectrometry. Peptides sequences identified using mass spectrometry are indicated with asterisks. The peptides detected in the hybrid degradation product by mass spectrometry are annotated on a full–length FH/FHR3 hybrid protein. CCPs that cannot be directly inferred from mass spectrometry data are outlined with a dashed line. A molecular mass of approximately 120 kD is consistent with an approximately 17 CCP protein. (B) Decay acceleration assays on sheep erythrocytes. The purified FH/FHR3 hybrid from the patient showed impaired cell surface complement regulation compared with wild type (WT) FH purified from control. Alternative pathway convertase (C3bBb) was formed on sheep erythrocytes. Cells were incubated for 15 minutes with dilutions of purified FH/FHR3 hybrid and WT FH before triggering lysis with NHSΔBΔH. Maximal lysis occurs in buffer-only (0 mM FH) conditions. Addition of WT FH caused decay of the C3 convertase and decay of convertase resulting in inhibition of lysis. The FH/FHR3 hybrid was up to 2-fold less efficient at inhibiting lysis. (C) C3b cofactor activity on sheep erythrocytes. WT FH and purified FH/FHR3 hybrid were tested for the ability to act as a cofactor for factor I–catalyzed inactivation of C3b deposited on the surfaces of sheep erythrocytes. The C3 convertase (C3bBb) was formed on residual C3b, and lysis was triggered by adding NHSΔBΔH. Maximal lysis occurs in the presence of buffer only (0 mM FH). The addition of WT FH and factor I produces iC3b, which decreases convertase formation and subsequent lysis, and this is shown as increasing amounts of inhibition of lysis (expressed as percentage of maximal lysis) after incubation with factor I and WT FH (black circles) or FH/FHR3 hybrid (white circles). The FH/FHR3 hybrid can be seen to be markedly less active than WT.