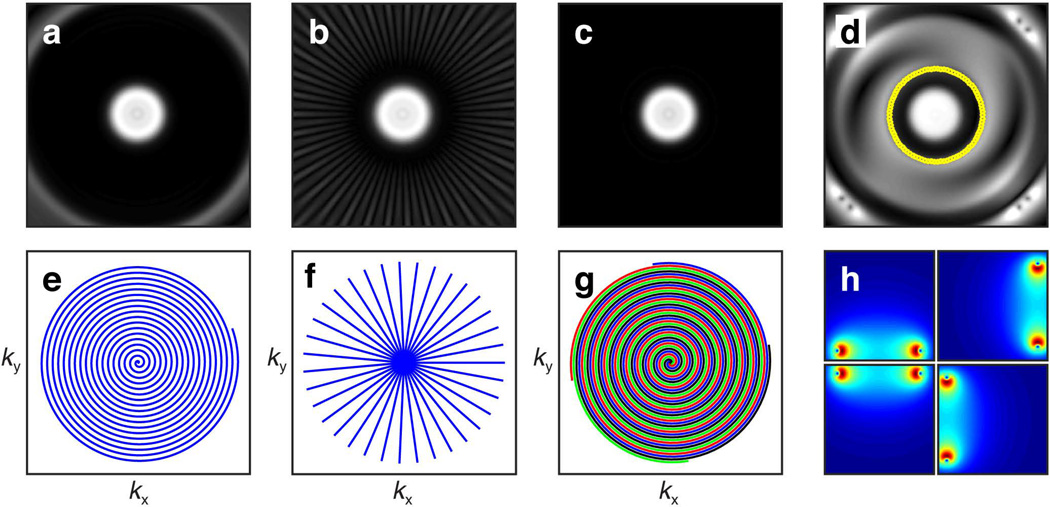
Figure 6.
Excitation profile of the 2D HS1 resulting from (a) spiral sampling, (b) multiscan radial sampling, and (c) interleaved spiral sampling demonstrates the ability to use multi-shot/interleaved excitation sampling schemes to reduce pulse width. In comparison to (e) single-shot spiral sampling of pulse width 16.384 ms, (f) multiscan radial sampling decreased the pulse width to 1.024 ms at the expense of requiring 35 excitations, while (g) interleaved spiral sampling decreased the pulse width to 4.096 ms at the expense of requiring 4 excitations. (d) Multicoil parallel excitation profile of the 2D HS1 pulse using ROI specification[18] (indicated by yellow circle). (h) Four coil elements placed along the sides of a square were used to accelerate excitation. Parallel transmission has the advantage of accomplishing single shot excitation with a reduced pulse width (4.096 ms) by taking advantage of the individual coil B1+ profiles.