Fig. 3.
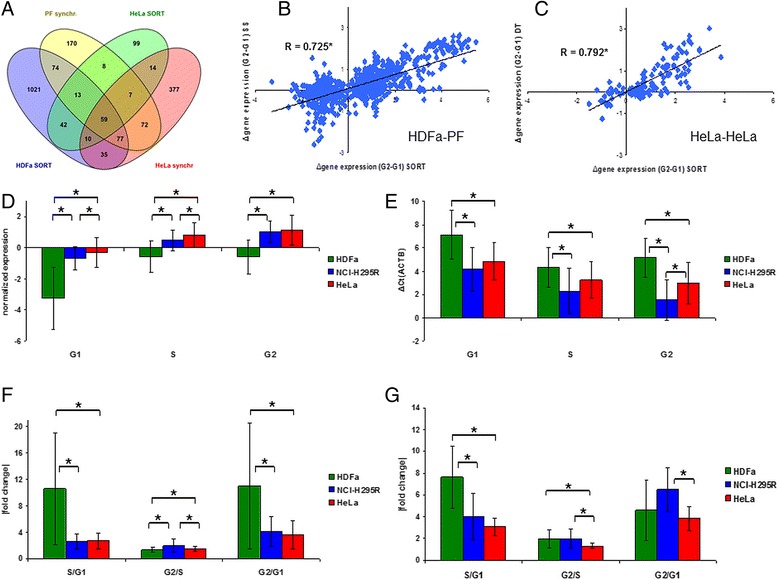
Comparison of cell cycle dependent gene expression observed by cell cycle sort and synchronization experiments and analysis of gene expression dynamics during the cell cycle in various cell types. Panel a: Venn diagram of cell cycle dependent genes detected in cell cycle sorted primary fibroblasts (HDFa SORT), in synchronized primary fibroblasts (PF synchr – data from [5]), in cell cycle sorted HeLa cells (HeLa SORT) and in synchronized HeLa cells (HeLa synchr – data from [4]). Intersections present the number of commonly found genes. For gene lists see Additional 1: Table S4. Panels b-c: Correlation analysis of gene expression differences using normalized expression values obtained from microarray experiments. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated from Δ(G2-G1) expression changes detected by cell cycle sort and former synchronization experiments in primary fibroblasts (synchronization method: serum starvation – SS, Panel b) and HeLa (synchronization method: double thymidine block – DT, Panel c) cells. Correlation coefficients are displayed. Asterisks mark statistical significance (p < 0.05). For additional correlation calculations see Additional 2: Figures S3 and S4. Panels d-e: Analysis of normalized gene expression values of different cell types. Normalized gene expression of 127 cycling genes exported from microarray data (Panel d) and 10 cycling genes exported from qRT-PCR data (Panel e) were analyzed. Note the lower ΔCt(ACTB) values mean higher expression values. Error bars show standard deviation. Asterisks mark statistical significance (p < 0.05). Panels f-g: Analysis of mean gene expression fold change between cell cycle phases of different cell types. Absolute values of fold change of 127 cycling genes exported from microarray data (Panel f) and 10 cycling genes exported from qRT-PCR data (Panel g) of cell cycle sort experiments were analyzed. Error bars show standard deviation. Asterisks mark statistical significance (p < 0.05)
