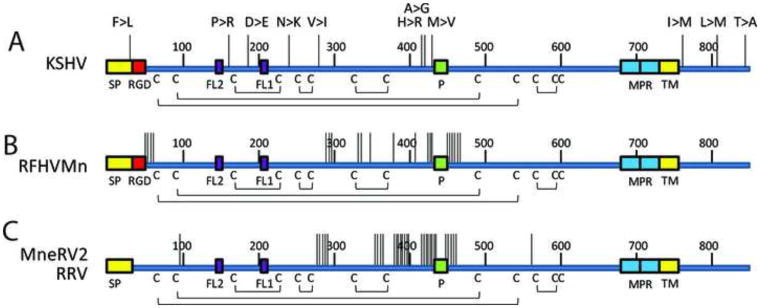
Figure 11.
Genetic variants in the human and macaque rhadinovirus gB homologs.
The non-synonymous sequence variants between A) KSHV strains (GK18, VG1, JSC1 and 16 Zambian KSHV variants), B) two RFHVMn strains (M78814 and 442N), C) two RRV strains (17577 and H2695) and two MneRV2 strains (J97167 and 98126) were mapped onto the linear gB sequence. Each vertical line represents a variant, and the amino acid changes from the GK18 reference sequence are shown for KSHV: F19>L (ZM95), P140>R (VG1, ZM4, 27), D192>E (ZM95, 102, 116, 117, 118), N236>K (ZM91), V270>I (VG1, ZM4, 27), H412>R (VG1, ZM4, 27), A413>G (ZM106), M431>V (VG1, ZM4, 27, 114, 128, 130), L759>M (JSC-1). The positions of the signal peptide (SP), RGD motifs, fusion loops (FL2, FL1), furin protease cleavage site (P), membrane proximal amphipathic domains (MPR), hydrophobic transmembrane domains (TMH) and cysteines and disulphide bonding pattern are indicated. Numbering is from the KSHV sequence (Fig. 3).