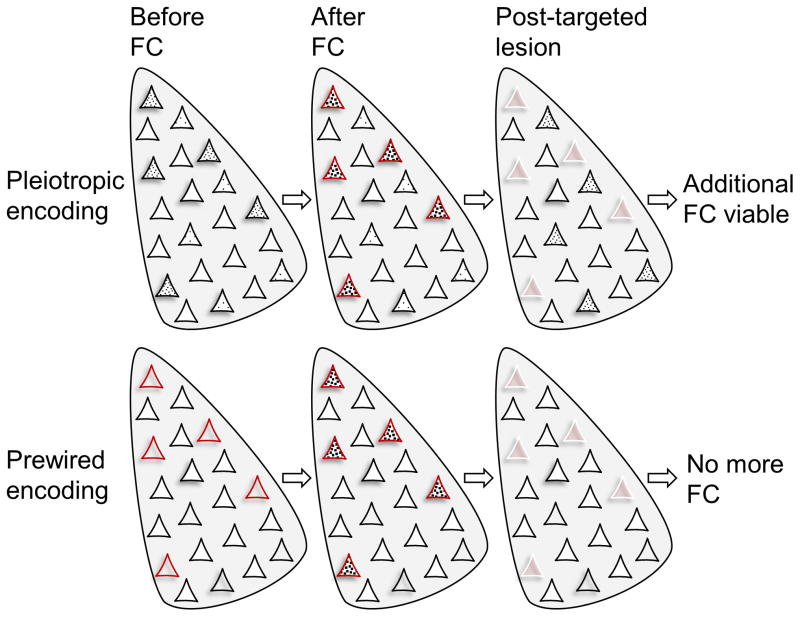
Figure 3. Two fear memory encoding schemas.
(Top) Amygdalar neurons with relatively higher CREB activity (denoted by black dots) form a memory trace (an engram) following fear conditioning (fear conditioning). When those neurons are ablated (represented by white borders), the fear memory is abolished. However, those remaining neurons with higher CREB activity can then support new fear memory formation. (Bottom) Small subset of amygdalar neurons that receive both CS and US information are biologically predetermined, irrespective of relative basal CREB level, to support fear memory. When those neurons are eliminated, fear memory cannot be formed regardless of increasing CREB activity in remaining neurons.