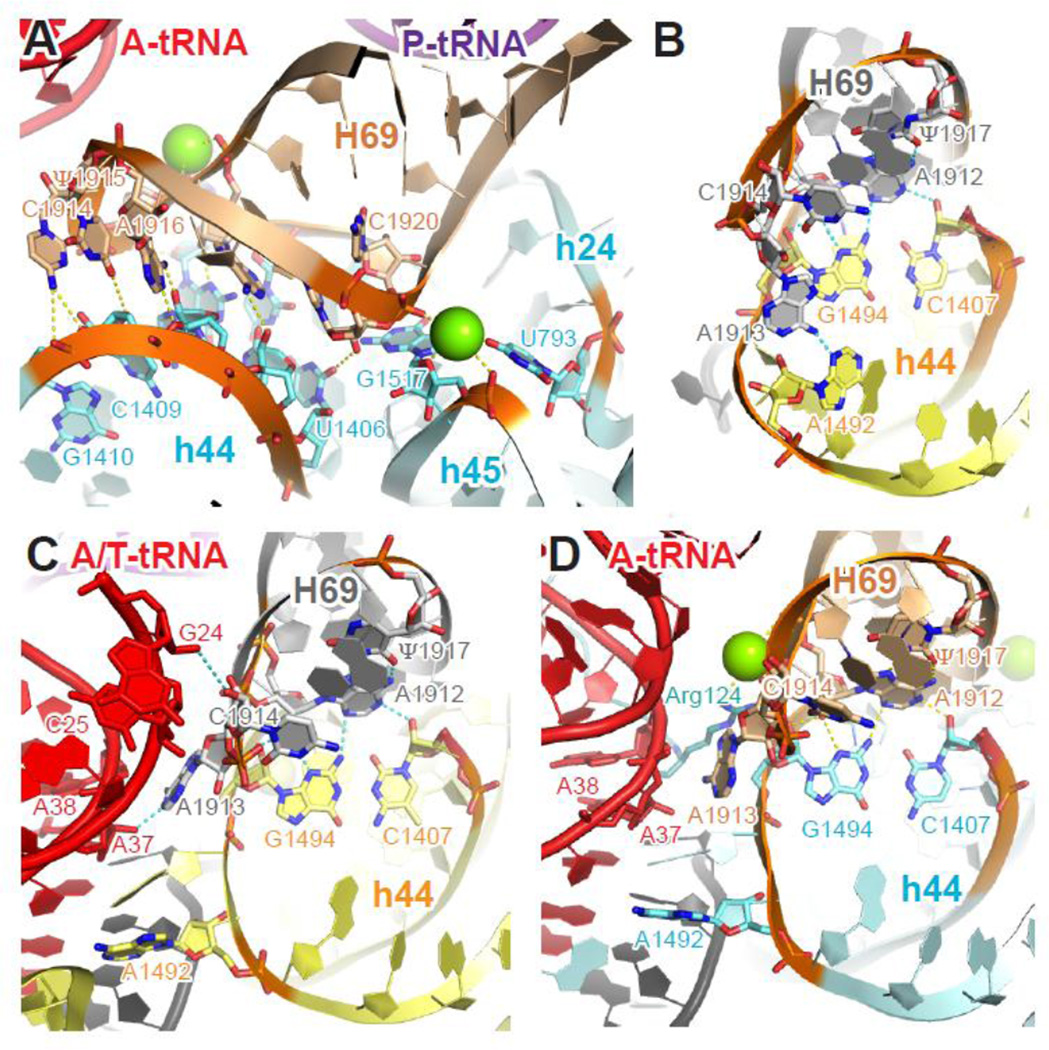
Figure 4. Molecular interactions and conformational changes at bridge B2a/d.
(A) Tertiary structure of H69 of the 23S rRNA and h24, h44, h45 of the 16S rRNA in the context of classic-state 70S ribosome. (B–D) Conformational changes of h44 (A1492) and H69 (A1913 and C1914) during decoding. In the ribosome with a vacant A site (B), A1492 of h44 interacts with A1913 of H69 at bridge B2a/d. In the ternary complex-bound ribosome trapped with kirromycin (C), the aa-tRNA is in a distorted A/T conformation, A1492 flips out of h44 and loses its interaction with H69, while A1913 and C1914 contact nt 37–38 and 24–25 of the A/T-site tRNA, respectively. When the aa-tRNA has been accommodated into the A/A site (D), A1492 of h44 and A1913 of H69 remains interact with the A-site tRNA, while C1914 of stacks back into H69. Cyan (T. thermophilus), yellow (E. coli), 16S rRNA; wheat (T. thermophilus), gray (E. coli), 23S rRNA; red, A- or A/T- site tRNA; purple, P-site tRNA; black, mRNA; green sphere, Mg2+. Residues involved in tertiary interactions are shown in sticks and colored by elements (red, oxygen; blue, nitrogen). Potential hydrogen bonds are marked with yellow (T. thermophilus) or cyan (E. coli) dashed lines. Panels A and D were generated using PDB entries 2WDK and 2WDL 39, panel B was generated using PDB entries 3R8O and 3R8T 24, and panel C was generated using EMDB entry EMD-2847 43.